Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
A
B
C
D
200nm
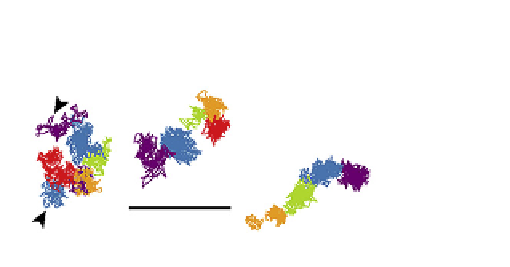
FIGURE 9.16
Four characteristic motions observed by SPT for E-cadherin in the plasma membrane of a cultured
mouse karatinocyte. The four motions are: A: stationary mode; B: simple Brownian diffusion mode; C: directed
diffusion mode; and D: confined diffusion mode. SPT trajectories of E-cadherins were recorded for 16.7 s (500 video
frames)
[25]
.
that of freely diffusing lipids in artificial bilayers
25
µ
s resolution, 62 ms observation
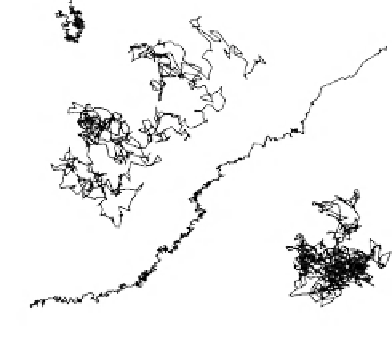
Start
Compartment Size : 230 nm
Residency Time : 11 ms
D
100
µ
s
: 5.4
µ
m
2
/s
1
µ
m
Finish
Typical trajectories of DOPE
FIGURE 9.17
Hop diffusion of the membrane phospholipid DOPE (18:1,18:1 PE). DOPE spends most of its time
trapped in a compartment (~11 ms) before hopping out and diffusing to another compartment where it is again
trapped. DOPE diffuses as fast within the confined domains as it does in a protein-free lipid bilayer
[57]
.
The 'fence' (corral) model for membrane structure possesses some major questions that
must be addressed. For example, what effect does the relatively enormous attached gold
particle have on the measurements? Since it is likely that only the plasma membrane has
a close association with the cytoskeleton, do the other intracellular membranes display
corrals? How does 'raft' theory fit in with 'fence' theory? Does one negate the existence of
the other or are they compatible?
Membrane Lateral Diffusion Rates: Conclusions
The Frye-Edidin experiment proved that membrane proteins were free to diffuse laterally
in the cell plasma membrane at a rate sufficient to completely encircle a bacterial cell in