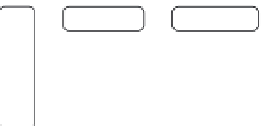Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
N-acetyl
galactosamine
glucose
galactose
galactose
sialic acid
GM
1
galactose
N-acetyl
galactosamine
glucose
galactose
sialic acid
GM
2
N-acetyl
galactosamine
glucose
galactose
sialic acid
GM
3
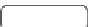
FIGURE 7.5
Enzymatic degradation of the ganglioside GM
1
/
GM
2
/
GM
3
.
1/27 of normal adults of Eastern European (Ashkenazi) Jewish origin and is 100 times more
prevalent in Jews than other populations.
Approximately 50 lysosomal storage diseases have now been identified, all resulting in the
accumulation of unhydrolyzed membrane sphingolipids. These relatively rare, incurable
genetic diseases occur in less than 1 in 100,000 births. They primarily affect children, resulting
in premature deaths, often within a few months or years of birth.
Table 7.1
lists a few of the
better known LSDs.
C. GLYCOPROTEINS
Most plasma membrane proteins have attached sugars, all of which face the outside. On
the plasma membrane outer surface there is a higher percentage of proteins with attached
sugars (glycoproteins) than lipids with attached sugars (glycolipids). Glycoproteins
[9,10]
are ubiquitous in nature, although they are relatively rare in bacteria. The sugars are attached
co- or post-translationally to a protein through either the nitrogen of asparagine or the
oxygen of serine, threonine, hydroxylysine, or hydroxyproline via a process known as glyco-
sylation (
Figure 7.6
). Attachment to asparagine is known as N-glycosylation and to serine,
threonine, hydroxylysine, or hydroxyproline as O-glycosylation. N- and O-glycosylations