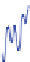Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
1
0.5
0
C
20
C
30
C
40
C
50
−0.5
−1
−1.5
Jan
Apr
Aug
Dec
2008
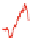
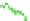
Fig. 17
Time variations of low degree coefficients expressed in geoid height in millimeter, dif-
ference between neglecting and including loading, in
black C
20
,in
blue C
30
,in
red C
40
and in
green C
50
the flow that results from, or is in balance with, a sea surface slope. Baroclinic is the
depth-dependent part of the flow and results from the density distribution within the
ocean and tries to cancel the sea surface flow. Commonly the barotropic motions are
fast (hours to days) such as tides, although they include a small baroclinic contribu-
tion. The El Niño (Hurrell and van Loon
1997
) for example is a mainly baroclinic
phenomenon with its slow motions.
Compared to the atmosphere, the time-variable mass signal of the ocean is rather
small, the RMS surface mass variability is typically only 2-3 cm (Wahr et al.
1998
).
Still, ocean signals are evident in GRACE data and have to be considered and cor-
rected. There are various ways to model the oceanic response due to atmospheric
forcing, here only a short overview shall be given:
•
Non-inverted barometer
(NIB): Atmospheric pressure variations are fully trans-
mitted to the sea floor and the oceanic response is the same as for the solid Earth.
•
Inverted barometer
(IB): Pressure variations in the atmosphere
p
are compen-
sated by static variations of the sea depth and the pressure on the sea floor, i.e.,
the ocean bottom pressure, does only change to a minor extent corresponding to
a mean surface pressure over all the entire world ocean (Dickman,
1988
). In the
simplest case IB assumes 1 cm change in sea depth due to 1 hPa change in the
atmospheric pressure:
Δ
h
w
=−
Δ
p
ρ
w
g
0
δ
(39)
where
ρ
w
is the sea water density,
g
0
the Earth mean gravity acceleration, and
respectively
h
w
the change in sea depth, respectively.
However the ocean does not respond perfectly like the IB simulates, especially in
the tropics and in the southern ocean (Ponte and Gaspar
1999
), but also shallow
δ