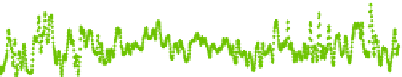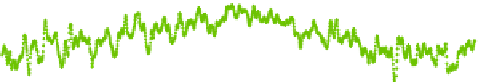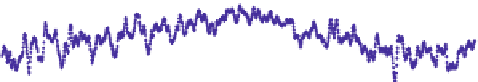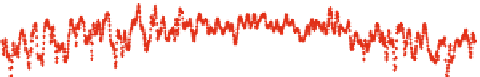Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
10
0
−10
5
0
−5
5
0
−5
2009
2009.2
2009.4
2009.6
2009.8
2010
Year
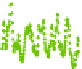
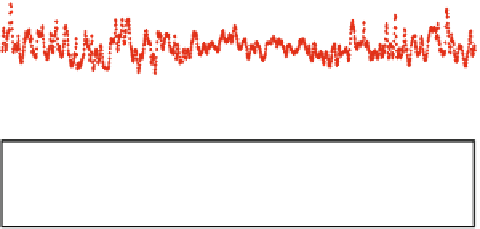
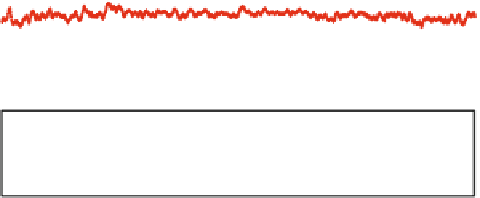
Fig. 8
APL displacements at Algonquin Park (ALGOPARK), Canada in
radial
and
horizontal
directions (unit mm) determined by the three services: Luxembourg (
green
), Petrov and Boy (
blue
)
and Vienna (
red
)
be due to different data input (surface versus pressure level, NCEP versus ECMWF)
and the land-sea masks used.
2.2 Empirical Model
From Sect.
2.1
, it can be seen that APL effects primarily cause vertical displace-
ments of the Earth's crust and therefore it is possible to determine linear regression
coefficients between the size of the vertical displacement and surface pressure vari-
ation. To estimate the regression coefficients, Rabbel and Zschau (
1985
) utilized
a geophysical approach (Sect.
2.1
) with idealized Gaussian pressure distributions
P
where
P
m
is the maximum pressure anomaly at the center
of the geometric distribution of cyclones or anticyclones,
r
is the distance from the
center of the distribution, and
r
o
is the scale length. They found that in general the
line of regression between surface pressure and the vertical displacement has the
form
P
m
exp
−
r
2
(
r
)
=
r
o
r
)
−
r
)
]+
U
r
(
)
=
C
1
[
(
P
ref
(
r
P
C
2
P
m
(12)
where
C
1
and
C
2
are the coefficients which are dependent on
r
o
and
P
(
r
)
P
m
, respectively.
They concluded that there is no unique single regression coefficient between local
displacements and local surface pressure and that it is therefore also necessary to