Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
1.6
2.4
Alkali-P
i
Acid-1-P
P
50
1.2
2.0
P
50
P
15
0.8
1.6
P
15
P
0
0.4
1.2
P
0
0.0
0.8
2.0
0.7
Alkali-P
o
Acid-2-P
1.9
P
50
0.6
1.8
P
15
0.5
1.7
P
0
0.4
1.6
1.5
0.3
45
85
6.0
P
0
Fe(III)
5.5
35
75
Fe(II)
5.0
P
15
25
65
4.5
P
50
15
55
4.0
5
45
3.5
02468 0
02468 0
mm from root plane
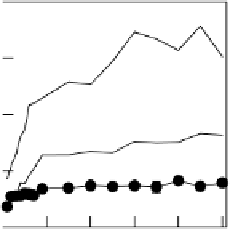
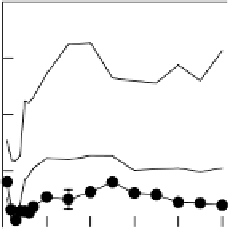
Figure 6.21
Profiles of P, Fe and pH near a planar layer of rice roots in contact with
flooded soil fertilized containing 0, 15 or 50mg P kg
−
1
for 6 weeks. The P pools mea-
sured sequentially were: readily available P extracted by anion-exchange resin (negligible
at all P levels and therefore not shown); readily acid-soluble P (Acid-1-P), extracted
by anion-exchange resin
H
+
-form cation-exchange resin; alkali-soluble inorganic P
(Alkali-P
i
), by 0.1M NaOH; alkali-soluble organic P (Alkali-P
o
), by digesting the previous
extract and subtracting the alkali-soluble inorganic P; the more recalcitrant acid-soluble
P (Acid-2-P), by 1M HCl
+
1MH
2
SO
4
. (Differences between P levels not significant
for Fe and Alkali-P
o
) (Saleque and Kirk, 1995). Reproduced by permission of Blackwell
Publishing
+