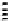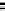Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
2
√
Dt
+
a
until it coincides with the boundary with
the equivalent cylinders around adjacent roots, at which point,
x
=
value of
x
increases as
x
=
1
/
√
πL
V
.In
the experiments, N as urea was mixed into the soil so that the concentration in
the floodwater was negligible. The urea N was all hydrolysed to NH
4
+
within a
few days.
The results are shown in Figure 6.8. They indicate that it would have been nec-
essary for the whole of the measured root length to have been active in uptake
to achieve the measured uptake rates, even though very large root length densi-
ties developed—up to 30 cmcm
−
3
, which is near maximal values for the upper
10 cm of soil under field conditions (Matsuo and Hoshikawa, 1993, Chapter 2,
Section 2), and uptake per unit root length was near maximal.
This is somewhat surprising: in dryland crops the total root length is generally
far larger than necessary to account for N uptake. An important difference is
that, as a result of NH
4
+
adsorption on the soil solid, unlike for NO
3
−
,the
concentration of NH
4
+
in the soil solution is less than
K
m
for high affinity NH
4
+
transporters in the root and so
V<V
max
and a larger root length is required.
(a)
(b)
10
2.0
8
1.5
6
1.0
4
0.5
2
0.0
0
(c)
(d)
5000
5000
−
N
+
N
1000
1000
500
500
100
100
20
30
40
50
20
30
40
50
Time (days after germination)
Figure 6.8
The time-course of (a) N uptake, (b) soil solution NH
4
+
, and (c) and (d) root
length density in pots of flooded soil planted with rice with
(
Ž
)
and without
(
ž
)
added N. In (a), lines are fitted logistic curves, slopes of which give values of d
U
/d
t
in Equation (6.10). In (b), solid horizontal lines are
C
L
; broken lines
C
La
calculated
with Equation (6.11). In (c) and (d), the lines indicate the minimum root length densities
required to explain uptake calculated with the measured
C
L
values
±
SE
(full lines) and
C
L
derived from exchangeable NH
4
+
values
±
SE
(Kirk and Solivas, 1997). Reproduced
by permission of Blackwell Publishing