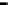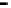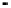Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
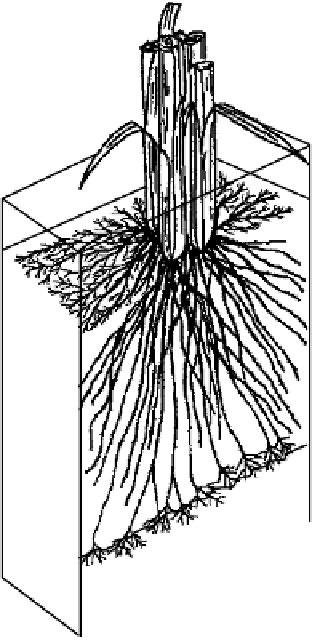
Superficial roots
in floodwater
and oxic soil
Floodwater
Oxic surface
soil
Primary roots
(with laterals)
in anoxic soil
Anoxic soil
Fine roots
penetrating
plough pan
Plough pan
Oxic
subsoil
Figure 6.4
Root system of the rice plant (Kirk, 2003). Reproduced by permission of
Blackwell Publishing
where
L
VL
is the length density of laterals in the cylinder of soil occupied by
them,
k
is a coefficient, equivalent to the distance at which
L
VL
(r)
=
0
.
25
L
VLmax
,
and
r
0
<r
≤
r
lat
. If the cylinder has outer radius
x
and inner radius
a
P
(i.e. the
radius of the primary root), and
x
and
a
P
are constant along the root length, then
the total length density of primary and lateral roots at distance
r
from the centre
of the hill is
2
πr
2
1
+
π(x
2
(k
+
r)
2
r
2
N
−
a
P
)L
VLmax
L
V
(r)
=
(
6
.
4
)
Equation (6.4) gives reasonable fits to measured profiles of
L
V
with depth in
the field.
Structure of an Individual Root and its Laterals
The porosity of the cortex, permeability of the root wall and the coverage of
the root with laterals vary along the root length, with a much smaller porosity,