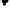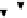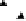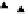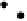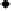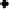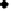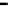Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
8
12
16.5 mM
at 0.5 wk
10
6
39
8
25
18
23
21
4
6
1
23
4
2
28
2
21
1
2
14
26
27
0
0
02468 0 2 4 6
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
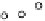
(c)
140
120
Org C
(%)
Active
Fe (%)
Soil
pH
100
1
7.6
2.3
0.18
1
14
4.8
2.8
2.13
80
18
5.6
6.0
0.27
21
4.6
4.1
2.78
60
23
5.7
8.0
0.47
25
4.8
4.4
0.18
25
26
7.6
1.5
0.30
40
27
6.6
2.0
1.60
28
4.9
2.9
4.70
20
26
27
14
29
5.8
7.7
1.80
39
8.1
2.0
-
0
02468 0 2 4 6
Time (weeks after flooding)
Figure 4.11
Changes in (a) NH
4
+
,(b)SO
4
2
−
and (c) P in the soil solution of various
soils following flooding (modified from IRRI, 1964, 1965). Reproduced by permission of
IRRI
of NH
4
+
on the soil exchange complex. Figure 4.11 shows changes in NH
4
+
in
solution following submergence of a range of soils.
4.3.3
TRANSFORMATIONS OF SULFUR
The stable form of sulfur under moderately strong reducing conditions
(
pe
<
−
3
)
is hydrogen sulfide, H
2
S, which is readily soluble and under non-acid conditions