Database Reference
In-Depth Information
FIGURE 2.14
Basic syntax of SQL/MR query function. (From E. Friedman et al.,
PVLDB
,
2(2), 1402 -1413, 20 09.)
plan-time. This also increases reusability as the same SQL/MR function can be used
on inputs with many different schemas or with different user-specified parameters.
In particular, SQL/MR allows the user to write custom-defined functions in any pro-
gramming language and insert them into queries that leverage traditional SQL func-
tionality. A SQL/MR function is defined in a manner that is similar to MapReduce's
map and reduce functions.
The syntax for using a SQL/MR function is depicted in Figure 2.14 where the
SQL/MR function invocation appears in the SQL
FROM
clause and consists of the
function name followed by a set of clauses that are enclosed in parentheses. The
ON
clause specifies the input to the invocation of the SQL/MR function. It is important
to note that the input schema to the SQL/MR function is specified implicitly at query
plan-time in the form of the output schema for the query used in the ON clause.
In practice, a SQL/MR function can be either a mapper (
Row
function) or a reducer
(
Partition
function). The definitions of row and partition functions ensure that they can
be executed in parallel in a scalable manner. In the
Row Function
, each row from the
input table or query will be operated on by exactly one instance of the SQL/MR function.
Semantically, each row is processed independently, allowing the execution engine to con-
trol parallelism. For each input row, the row function may emit zero or more rows. In the
Partition Function
, each group of rows as defined by the
PARTITION BY
clause will be
operated on by exactly one instance of the SQL/MR function. If the
ORDER BY
clause
is provided, the rows within each partition are provided to the function instance in the
specified sort order. Semantically, each partition is processed independently, allowing
parallelization by the execution engine at the level of a partition. For each input partition,
the SQL/MR partition function may output zero or more rows.
2.4.8 h
aDooP
Db
Parallel database systems have been commercially available for nearly two decades
and there are now about a dozen of different implementations in the marketplace
(e.g., Teradata,* Aster Data,
†
Netezza,
‡
Ver t ica ,
§
ParAccel,
¶
Greenplum**). The
*
http://www.teradata.com/.
†
http://www.asterdata.com/.
‡
http://www.netezza.com/.
§
http://www.vertica.com/.
¶
http://www.paraccel.com/.
**
http://www.greenplum.com/.





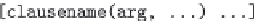


Search WWH ::

Custom Search