Database Reference
In-Depth Information
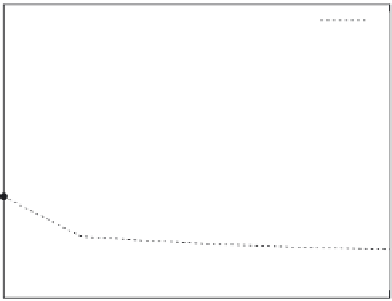
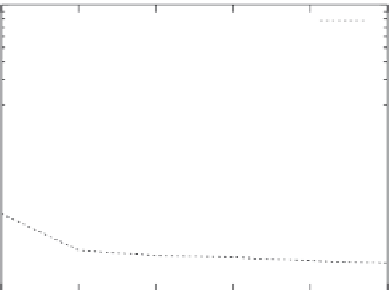
This overhead becomes more visible for the smallest skip offset of 20 MB. This
was expected since the Rabin fingerprint needs to be computed for a larger fraction
of the data. Somewhat more surprising was the reduction in throughput for the larg-
est skip offset of 60 MB. This is due to the fact that increasing the skip offset leads to
an increase in the average chunk size, which in turn leads to decreasing the amount
of parallelism toward the end of the data upload. We therefore found 40 MB to be a
reasonable compromise between these two negative factors.
4.6.5 w
ork
anD
t
Time
s
PeeDuP
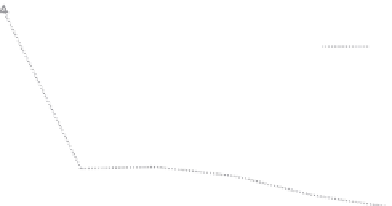
We report the speedup of Incoop relative to Hadoop in terms of work and time in
Figure 4.5a and b, respectively. The results show that incremental computations
Incoop are significantly faster than recomputing the data from scratch using Hadoop,
(a)
WordCount
BiCount
CoMatrix
K-Means
KNN
1000
100
10
1
0
5
10
15
20
25
Incremental changes (%)
(b)
100
WordCount
BiCount
CoMatrix
K-Means
KNN
10
1
0
5
10
15
20
25
Incremental changes (%)
FIGURE 4.5
Performance gains for Incoop in comparison to Hadoop. (a) Work speedups
vs. change size. (b) Time speedups vs. change size.





































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search