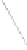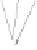Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
n = 3
, p=2 , therefore elements are 0,1,2,3.
Clock
3 2 0
T =
r = Rank = 2 , Depth = 3
3 1 2
Characteristic Polynomial = x
3
3
Cell 0
Cell 1
Cell 2
0 3 2
Minimul Polynomial = x
p
3
1
2
No. of predecessor = 2 = 4
1 1 0
1 1 1
0 1 1
0
3
3
D =
2
2
0
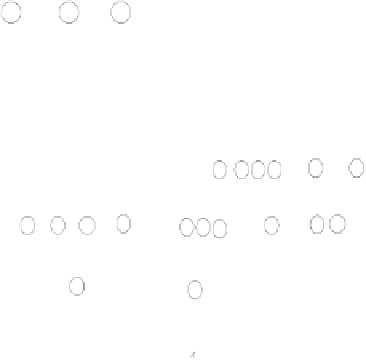
No. of Non reachable states = 48
Cyclic States = 000
Attractor = 000
0
p
F =
At GF(2 ) field where
p=2,
0
0
2
3
1
0
1
0
a =
=
1
1
a =
=
0
1 1
a =
=
1 0
0 1
=
0
0
2
3
1
0
0
211
133
........3
233
121
310
002
200
....
222
020
332
103
311
.............
322
122
001
313
022
100
...
032
221
010
302
033
110
202
321
022
101
213
011
220
303
132
330
..............................2
312
123
.......................................................................1
231
000
.................................................................................................................................0
Fig. 2.
State Transition Diagram of 3-cell GF(2
2
)
SACA
2.2
Single Attractor Cellular Automata (
SACA
)
The CA belonging to this class and its complemented counterpart referred to
as Dual
SACA
display some unique features that have been exploited in the
proposed authentication scheme. The T matrix ofan n cell GF(2
p
)
SACA
is an
n × n
matrix with its elements in GF(2
p
). The rank, characteristic polynomial
and minimal polynomial ofthe
T
matrix are :
rank(
T
)=
n −
1, rank(
T ⊕
I)=
n
,
I
being the
n × n
identity matrix.
Characteristic polynomial =
αx
n
, Mimimal polynomial =
αx
n
, where
α ∈
GF(2
p
).
A few theorems are next introduced without proof. The proof is analogous to
GF(2) TPSA (Two Predecessor Single Attractor) CA noted in [2].
Theorem 1
: Ifthe rank ofthe characteristic matrix T ofan
n
cell GF(2
p
)
non-group CA is
n −
1, then each reachable state has 2
p
predecessors.
Theorem 2
: Depth ofan
n
cell
SACA
is equal to
n
The inversion vector F in the example
SACA
ofFig. 2 is an all 0's vector. A
non-zero F leads to its dual counterpart.
Dual SACA
A dual
SACA
also referred to as
SACA
results from an introduction of non-
zero inversion vector F with the characteristic matrix T ofthe
SACA
.
SACA
has identical state transition behavior as that of
SACA
with change ofrelative