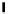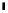Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
2.5
0.3
fft(µ)
2
0.25
1.5
1
0.2
µ
0.5
0.15
0
0.1
−0.5
0.05
−1
−1.5
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
20
40
60
iterations
ω
3
fft(µ)
0.4
2
1
µ
0
0.2
−1
−2
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
20
40
60
ω
iterations
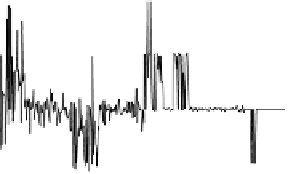
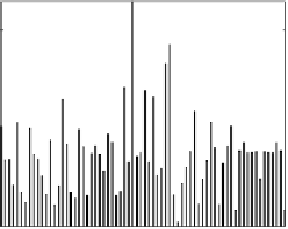
Fig. 3.
Total mobility at a door of width 3 in a 200
×
50 hexagonal lattice with a wall
at
x
= 100. The bottom plots are the signal and its Fourier transform fft(
µ
) obtained
with individuals who do not interact. This measure serves as a test of the noise at
the door due to the initial random configuration of the crowd. The top plots are the
ones with an interacting crowd: we observe higher amplitude peaks at low frequency
showing that the two crowd gain access through the door with oscillations.
However, it is more probable that in reality this should dynamically depend on
the situation of an individuals e.g. even in a dense crowd backtracking just before
reaching an exit door is never considered while it might be an issue before.
The disorder parameter
ξ
represents the ability to keep focused on the favorite
direction(
ξ
= 0) or to consider neighboring cells i.e. directions(
ξ>
0). Therefore
the effect of
ξ
can be viewed as the ability to explore the environment with the
side effect of diffusing the individual. We consider this as a way of modeling panic.
The definition of panic is however situation dependent: a stressed individual with
a clear destination will not consider any other direction but his favorite one,
namely
ξ
= 0; on the contrary if there is no clear destination, one might choose
to explore all directions, namely
ξ
=
z/
2, in the hope of finding a hidden way
out.