Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
H
NH
H
N
Cl
-
HN
HN
H
2
PO
4
-
Cl
-
NH
NH
HN
O
N
O
N
N
H
H
Cl
-
Cl
-
NH
N
O
O
N
HN
NH
H
2
PO
4
-
NH
N
N
N
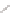
Figure 2.39 Cyclic oligopyrroles twist into loops in figures of eight and encapsulate anions
by hydrogen bonds in two distinct cavities.
anions, such as dihydrogenphosphate and hydrogen sulfate. In contrast, no binding is
observed with chloride, bromide and nitrate, probably due to the shape mismatch of these
anions to the binding pocket generated by a tetrahedral template.
Gale and coworkers reported a polymer consisting of 3,4-dichloro-2,5-diamido-
substituted pyrrole units (Figure 2.40a) [105], which, on the addition of fluoride ions,
dimerizes in an orthogonal manner via NH . . . N
hydrogen bonds. Maeda and
coworkers reported a polymeric network formed by chloride bridges with BF
2
complexes
of acyclic dipyrrolyldiketones (Figure 2.40b) [106].
2.5 Applications
Interesting applications of foldamers include the preparation of pharmacologically active
compounds, because one of the major concerns in the development of pharmaceutically
potent peptides as drugs is their poor proteolytic stability and rapid degradation.
Amazingly, the introduction of single acyclic b-amino acid residues into major histo-
compatibility complex (MHC) class I binding peptides led to increased stability of these
peptides against enzymatic cleavage [107]. Gellman and coworkers [108] first investigated
the proteolytic stability of a/b-peptides containing cyclic b-residues. Along this line,
another study concluded that b-amino acids incorporated within a peptide sequence can
protect the amide bonds of neighboring a-amino acids [109]. If more alterations are intro-
duced in the backbone, more results may be obtained. For instance, a/b-peptides with a 1 : 1
backbone alternation were shown to exhibit distinct antibacterial activity [110]. Addition-
ally, some studies of the Gellman group provided experimental support for the hypothesis
that the formation of a globally amphiphilic helix is not required for host-defense peptide
mimicry [111], as amphiphilic conformations of random copolymers without any helical
structure were also proven to exhibit potent antibiotic activity (Figure 2.41).
Another very important goal is the formation of discrete tertiary structures.
Most foldamer research to date has focused on the formation of secondary structures,
but creating foldamers with a discrete tertiary structure has long been recognized as a


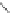







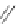
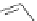


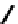


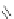
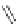


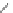









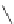








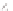

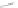








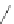














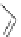

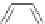

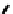

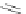




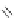

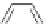
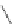

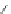
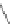
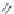





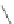
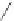
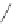

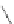


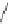


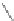





































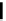






Search WWH ::

Custom Search