Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
H
H
R
N
H
R
γ
NH
CH
2
C
γ
H
θ
1
θ
2
ψ
R
H
φ
H
2
C
θ
1
θ
2
ψ
H
γ
α
N
C
α
H
H
β
φ
H
O
H
H
O
H
O
O
C
β
n
O
4
-peptide
(2.6 helix)
γ
θ
1
= +70°
θ
2
= +60°
ψ
= -140°
Σ
= -130°
φ
= -120°
H
R
N
H
H
NH
H
NH
NH
H
R
γ
R
H
θ
1
θ
2
φ
ψ
H
2
C
θ
1
'
ψ
'
RHC
H
N
HN
H
φ
H
O
θ
2
N
H
O
H
O
CH
2
H
O
O
n
N,N'-oligourea
(2.5 helix)
φ
= -100°
θ
1
= +55°
θ
2
= +85°
ψ
= -130°
Σ
= -130°
Figure 2.16 Comparison of main chain dihedral angles between helical
N,N
0
-linked oli-
gourea and g
4
-peptide backbones.
14-helical fold [59]. g-Amino acid residues within the 14-helix are characterized by large
c values
140
) [60]. The additional nitrogen was believed to act as a rigidi-
fying element by fixing the pseudo c angle to a value close to 170-180
. Detailed NMR
studies provided compelling evidence that enantiopure
N
,
N
0
-linked oligoureas adopt a
well defined and stable 2.5-helical fold, akin to the g
140
(or
4
-peptide 14-helix [61]. The helix
is right-handed with a pitch of about 5.1 A
and held by H-bonds closing both 12- and
14-membered rings (12/14-helix). The structural analogy between oligourea and the
g-peptide helical backbone is evident when comparing the main backbone torsion angles
(Figure 2.16).
2.2.6 Foldamers of
a
-Aminoxy Acids
a-Aminoxy acids are analogues of b-amino acids in which the b-carbon atom in the
b-amino acid backbone is replaced by an oxygen atom [62]. The first synthesis of an
a-aminoxy diamide was reported by Yang's group in 1996 [63]. Theoretical calculations
suggest that it adopts a rigid eight-membered ring hydrogen-bonded structure (so-called
a
N-O
turn) in its most favorable conformation (Figure 2.17). In the presence of side
chains,
ab initio
calculation results suggest that chiral
L
-a-aminoxy acids prefer a left-
handed chiral
N
-
O
turn.
The formation of a rigid a
N
-
O
turn structure in a-aminoxy diamides suggested that
oligomers of aminoxy acids might have interesting conformational features and prompted
their investigation. Thus, a series of oligomers was synthesized and subjected to confor-
mational studies as performed previously for a-aminoxy diamides (the longest one is
PhH
2
CO
O
OCH
3
CH
3
NH
O
O
H
N
O
H
N
O
H
N
O
HN
HN
HN
O
O
O
O
O
O
Figure 2.17 Some examples of dipeptides containing a-aminoxy acids (the a
N
-
O
turn is
shown).










































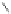










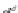













































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search