Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
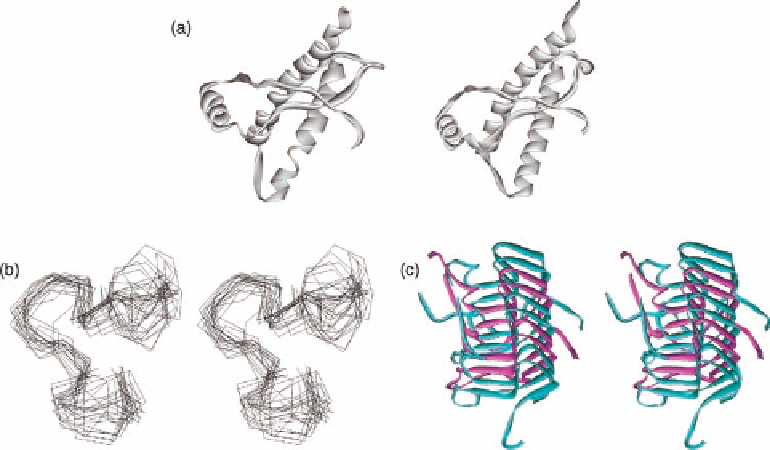
Figure 1.16 The NMR structures of recombinant human prion protein (globular domain
extending from residues 125-228) 1QM2 (a, left) and the crystal structure of the globular
domain of sheep prion protein 1UW3 (a, right). (b) Solution NMR structure of the octapeptide
repeats in mammalian prion protein (1OEI). (c) Solid-state NMR structure of amyloid fibrils
from the prion-forming domain of the HET-s protein (2RNM). Each monomer is highlighted in
a different color for clarity.
oxidative modification of PrP
C
which is also proposed to link to prion diseases [210]. How-
ever, PrP knockout mice are sensitive to Cu
2þ
-induced oxidative stress [211], which sug-
gests a possible anti-oxidation role of PrP
C
. Further research will be needed to fully
establish the biological function of this structurally two-faced Janus protein.
Cu
2þ
binding to PrP
C
triggers structural changes of the protein [212] which enhances
resistance against proteases [213] and is linked to the prion diseases. The N-terminal
domain of PrP
C
can bind up to six Cu
2þ
ions at physiological pH, with the first two Cu
2þ
ions binding to the amyloidogenic region (residues 90-126) and the rest to the four highly
conserved octapeptidyl repeats of PHGGGWGQ in residues 58-91 (Figure 1.16b) [214].
The four Cu
2þ
-octarepeats are not interacting with each other as they are magnetically
isolated [214a]. Synthetic octapeptide repeats show higher preference toward Cu
2þ
bind-
ing than other metal ions [215]. The crystal structure of the Cu
2þ
complex of the simple
peptide HGGGW reveals a square pyramidal coordination sphere with the equatorial sites
occupied by the His imidazole, two deprotonated Gly-amides, and a Gly-carbonyl and an
axial water H-bonded to the Trp indole [214a]. The similarity of the EPR spectra between
this simple complex and the Cu
2þ
-bound octarepeats suggests their similar coordination
sphere. Zn
2þ
also binds mammalian PrP with a weaker binding affinity than Cu
2þ
and can
affect Cu
2þ
binding modes in PrP [216]. However, there is no structure solved for the
entire protein or the N-terminus domain of this protein in either the native or the unfolded
Search WWH ::

Custom Search