Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
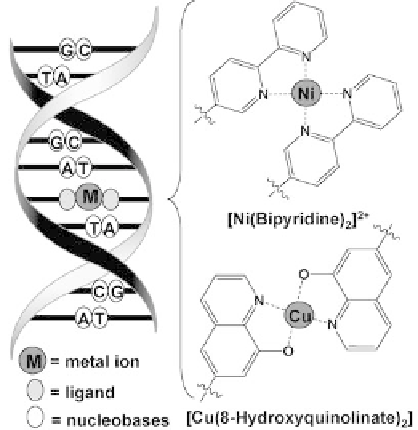
Figure 10.2 Cartoon representation of a nucleic acid duplex containing one metal-based
alternative base pair and examples of complexes formed with the two ligands from the two
single strands of the duplex.
high pH, which led to the coordination of one metal ion per nucleobase pair to form M-
DNA [6]. The structure, stability, and electronic properties of M-DNA have also been
evaluated by theoretical methods [7].
In 1999 Shionoya and collaborators published a paper containing the first mention of
the possibility to substitute nucleobase pairs in DNA with pairs of ligands and binding of
metal ions to these ligands to create metal-based alternative base pairs (bp) in duplexes
that contain both Watson-Crick and coordination bonds (Figure 10.2) [8]. They synthe-
sized several nucleosides and characterized metal complexes of these nucleosides [9].
In 2000 Schultz published the first DNA duplex containing a metal-mediated alternative
base pair based on a monodentate and a tridentate ligand coordinated to Cu
2þ
[10],
shortly followed by Tor [11] and Shionoya [12], who synthesized DNA duplexes modified
with a pair of two bidentate ligands that bound 3d transition metal ions. Since then, sev-
eral other groups including those of Switzer [13], M
uller [14], and Carell [15] have
applied this method to synthesize DNA duplexes containing one or several transition
metal ions. The same strategy was applied to the successful modification of peptide
nucleic acids (PNAs) [16], glycol nucleic acids (GNAs) [17], and locked nucleic acids
(LNAs) [18].
To date, several strategies have been used to create systems based on synergetic forma-
tion of hydrogen and coordination bonds, and p-stacking interactions (Figure 10.2).
Ligand incorporation in the center of nucleic acid oligomers (Figure 10.3a) was used to
create metal-containing, ligand-modified duplexes. In this approach, the coordination
complex formed between the metal ion and the ligands plays the role of an artificial base
pair and will be referred to as a metal-ligand alternative base pair or metal-mediated base
pair. Ligands have also been used as connectors of single-stranded (ss) nucleic acids
€
Search WWH ::

Custom Search