Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
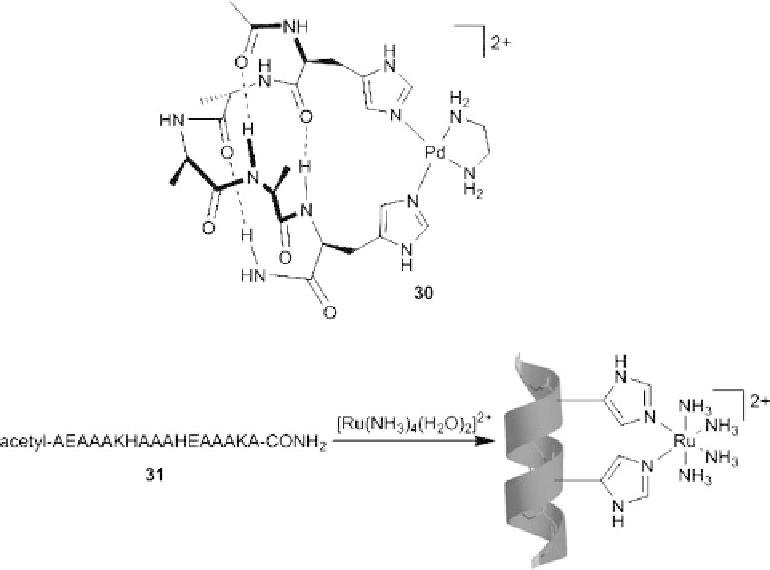
Scheme 8.4 Stabilization of a-helical peptide structures through coordination to histidine
residues located in
i
and
i
þ
4
position of the peptide strand.
the length of the connecting linkage. The introduction of two such units into the sequence
affords a compound with a high analogy to the ethylene diamine tetraacetate (EDTA)
chelator. The ethylene backbone of the parent EDTA is substituted by the short peptide.
Coordination of
32
to cobalt(II), nickel(II), copper(II), zinc(II), or cadmium(II) results
in the formation of coordination compounds with a preferred a-helical structure. CD
spectroscopy reveals that especially cadmium(II) is highly effective in stabilizing the
helix [54].
Other metal-binding amino acids for incorporation into peptides are the crown ether
A
and the cyclic triamine
B
. With peptides possessing two units of
A
no a-helix stabiliza-
tion was observed. However, Boc-Ala
3
-
A
-Ala
2
-
A
-Ala
3
-NHC
3
H
7
adopts a turn structure in
the presence of cesium cations [55].
In contrast, introduction of the triazanonane amino acid
B
into a peptide afforded a
helix-loop-helix motif upon addition of zinc(II) ions. The obtained complex is an active
catalyst for transesterification of phosphate esters [56].
Peptide
33
bears two peripheral phosphane units (Figure 8.21). Upon coordination
of rhodium(I) to the two diphenylphosphane units the a-helix structure of the peptide
is supported [57]. Derivatives similar to
33
were used as catalysts in hydrogenation
reactions [58].
Search WWH ::

Custom Search