Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
CONH
2
CONH
2
H
N
N
H
2
N
N
O
S
S
H
O
O
O
H
N
H
2
N
H
N
O
O
N
H
H
OH
R
N
O
OH
OH
H
O
O
H
O
OH
O
H
O
O
OH
O
N
H
2
(
1
)
Blm can bind various metal ions [92], including Mn
2þ
[93], Fe
2þ/3þ
[94], Co
2þ/3þ
[95],
Ni
2þ/3þ
[96,97], Cu
þ/2þ
[98,99], Zn
2þ
[98], Cd
2þ
[100], Ga
3þ
[101], and Ru
2þ
[102] as
well as the radioactive
105
Rh for radiotherapy [103], changing the conformation of the
molecule from a supposedly more extended form (
1
) to a more compact form (Figure 1.11,
green structure). Metallo-Blm has a distorted octahedral geometry with coordinated imid-
azole, pyrimidine, amines of b-aminoalamine, the amide nitrogen of b-hydroxyhistidine,
and possibly the amide group of a-
D
-mannose, as shown by optical, NMR, EPR, and elec-
tron spin-echo envelope modulation (ESEEM) spectroscopic methods, crystallography,
and chemical modeling [104-107]. This leaves an open or exchangeable site for O
2
or
peroxo binding. Similar coordination chemistry was also suggested for Zn
2þ
-Blm from 2-
D NMR [108], however excluding carbamoyl binding. The binding of Co
2þ
-Blm to DNA
via the bithiazole rings does not influence the metal coordination, whereas the binding of
O
2
-Co-Blm affects the bound O
2
where the unpaired electron resides [109].
Low-spin diamagnetic Co
3þ
complexes of Blm and analogues have structures similar
to Zn-Blm based on 2-D NMR spectroscopy, except the axial ligands [110,111]. The
structures of (DNA)
2
-Co
3þ
-Blm and (DNA)
2
-(HOO)Co
3þ
-Blm ternary complexes show
further structural changes upon DNA binding (Figure 1.11) [110,112]. The metal-binding
moiety is located in the minor groove of (DNA)
2
with the bithiazole rings intercalated into
the DNA double helix, rendering the bound peroxide close to the 4
0
-H of the scissile
ribose (
3A
). Conversely, the bithiazole is in the minor groove in Zn
2þ
-Blm-DNA [113].
Nevertheless, intercalation of bithiazole may not be necessary for DNA cleavage since
DNA cleavage by Fe-Blm is similarly effective compared to its derivative with the bithia-
zole tethered to a porous glass bead [114]. Fe
3þ
-Blm becomes low-spin (g
<
2.41, 2.18,
1.89) with a bound hydroxide at slightly alkaline conditions [115,116]. O
2
binds to Fe
2þ
-
Blm to afford a superoxide O
2
-Fe
3þ
-Blm complex based on its
57
Fe M
¼
ossbauer spec-
trum [117] which can afford an active HOO
-Fe-Blm complex toward DNA cleavage
[11b]. The paramagnetic Fe
2þ
-Blm (S
€
¼
2) with distance-dependent fast relaxing










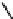



























Search WWH ::

Custom Search