Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
HN
O
HN
O
O
O
SH
NH
NH
NH
NH
SH
O
O
SH
HN
O
HN
O
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
SH
H
4
-
1
H
4
-
2
H
4
-
3
H
4
-
4
H
4
-
5
H
4
-
6
HS
HS
HS
HS
HS
O
HS
O
HN
O
= R
HN
NH
HS
SH
NH
O
NH
HS
SH
O
O
NH
HN
NH
SH
N
O
N
NHR
SH
SH
N
RHN
SH
H
6
-
7
H
6
-
8
H
6
-
9
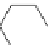
Figure 5.3 Bis- and tris(benzene-o-dithiol) ligands.
Apart from ligands containing exclusively benzene-
o
-dithiol groups, mixed benzene-
o
-
dithiol/catechol ligands like H
4
-
10
-H
4
-
13
(Figure 5.4) have been prepared from 2,3-
dimercaptobenzoic acid and functionalized catechol using standard protection group
chemistry [29].
5.2 Coordination Chemistry of Bis- and Tris(Benzene-o-Dithiolato) Ligands
5.2.1 Mononuclear Chelate Complexes
Depending on the topology of the ligand and the preferred coordination geometry of a
given metal ion, polydentate ligands can form several different coordination compounds.
Ligands with long and flexible backbones, such as H
4
-
14
and H
4
-
15
, react with Co
III
ions
under the formation of mononuclear chelate complexes. Both complexes (NEt
4
)[Co(
14
)]
and (NEt
4
)[Co(
15
)] have been obtained in a thermodynamically controlled ligand transfer
reaction utilizing (NEt
4
)
2
[CoCl
4
] and the halophilic di(titanocene) complexes of
14
4
and
15
4
(Scheme 5.2) [30].

























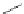









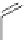

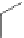
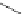





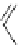

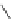

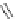
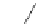

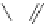

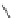

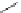
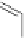
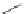



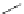

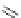



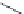









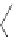
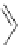

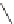
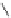










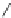


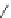
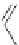














































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search