Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
0
K
2,gas
G
3+
gas
3
gas
6+
2 s
t
-
[Eu
L
]
Eu
ct
-
[Eu
L
]
+
3
0
0
G
(Eu
L
)
0
solv
G
(Eu)
G
(Eu
L
)
solv
2
3
solv
3
0
G
2,sol
3+
sol
3+
3
sol
6+
t
-
[Eu
L
]
+
Eu
ct
-
[Eu
L
]
2
3
sol
+
Eu
0
G
(b)
3,gas
6+
3+
gas
9
3 s
ct
-
[Eu
L
]
Eu
[Eu
L
]
+
2
3
gas
0
0
G
(Eu
L
)
0
solv
G
(Eu)
G
(Eu
L
)
solv
3
3
solv
2
3
0
G
3,sol
3+
sol
6+
9+
ct
-
[Eu
L
]
+
Eu
[Eu
L
]
2
3
sol
3
3
sol
+
Eu
Figure 3.18 Thermodynamic Born-Haber cycles for the successive complexation of Eu(III) to
(a)
t
-[EuL
3
]
3þ
to give
ct
-[Eu
2
L
3
]
6þ
and (b)
ct
-[Eu
2
L
3
]
6þ
to give [Eu
3
L
3
]
9þ
.
Reprinted with per-
mission from [52]. Copyright 2007 American Chemical Society.
compensate to some extent the above factors. Since we are dealing with metallo-organic
assemblies, let us investigate the predominant effect of electrostatic interaction on the
global free energy change.
For metallic cations considered as point charges, the magnitude of intermetallic inter-
actions in the gas phase can be calculated with Coulomb's law as the electrostatic work
D
E
MM
, which depends on the intermetallic distance. The transformation of Coulombic
interactions in the gas phase into free energy in solution can be done using a Born-Haber
cycle, as shown for several helical complexes [19,52]. A demonstrative example of this
procedure is shown in Figure 3.18. The related values of solvation energies can be esti-
mated from the Born equation using the hydrodynamic radii of diffusing supramolecular
complexes, which can be conveniently measured with diffusion ordered spectroscopy
(DOSY-NMR).
The values of Coulombic repulsions and the solvation energies are usually huge, but
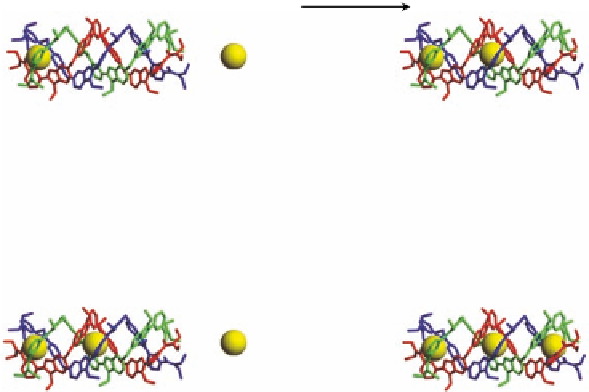
with opposite contributions. Therefore, the overall effect of homocomponent interactions
is of limited magnitude and depends on the charge distribution within the assembly, its
shape and the organization in solution [13]. The competition between electrostatic inter-
actions and solvation energies is illustrated in Figure 3.19 for dinuclear double-stranded
helicates, which differ in spacer length and thus in intermetallic distances, while other
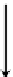
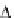





Search WWH ::

Custom Search