Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
TGF-β
Hedgehog
Smad
Wnt
Notch
Gli1 Slug/Snail
NF-B
ZEB
Snail
/
Slug
E-cadherin
Epithelial mesenchymal transition
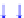
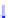
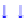
Figure 4.3
Pathways activated by Hh and TGF-β towards EMT. Here emphasised is the
interaction with Wnt and Notch in the downregulation of E-cadherin expression leading to the
manifestation of EMT. Certain miRNAs modulate ZEB expression and influence EMT. Indeed,
there is evidence that Notch, Wnt and TGF-β pathways might be integrated by Notch ligands.
cell migration. In parallel with Gli1 downregulation cells showed downregulation of
expression of Snail, MMP9 and enhancement E-cadherin expression (Wang et al.,
2010b). The expression of Gli1 has been found to correlate negatively with the expres-
sion of E-cadherin and positively with the tumour promoter S100A4 in primary hepa-
tocellular carcinoma tissues (Zheng et al., 2010). Liao et al. (2009) observed that
overexpression of PTCH/Gli1correlated with poor survival of ovarian cancer patients.
Also they found high levels of SHh mRNA in carcinomas as compared with normal
tissue and benign conditions. But Joost et al. (2012) reported that inhibition of Gli1
promoted EMT and further that decreased Gli1 levels corresponded with more aggres-
sive and metastatic phenotype in pancreatic ductal carcinoma. The latter progresses
from intraepithelial neoplasm through several steps with associated cellular changes; of
these mucin5AC expression is one. Gli1 increases MUC5AC expression in pancreatic
carcinoma cells and suppression of Gli1 and Gli2 negates this. Gli1-mediated upregu-
lation of MUC5AC also leads to localisation of E-cadherin to the membrane and con-
sequent decrease in E-cadherin-dependent cell adhesion and migration (Inaguma et al.,
2011). So it may be that pancreatic carcinoma represents a unique model. There is also
the possibility of a switch of signalling pathways.
These findings provide the background and serve also a prelude to the topic of
deployment of the amalgamation of Hh signalling with TGF-β and Wnt to target
them for inhibition. TGF-β upregulates the transcription of Gli1. The transcription
factors Slug/Snail which suppress E-cadherin also can downregulate Gli1 (Katoh and
Katoh, 2008, 2009). It would seem therefore that whereas in collusion Hh and TGF-β
could be functioning via the Smad/Wnt pathway to activate EMT, when TGF-β is
absent Gli1 activation might be suppressed by Slug/Snail. It ought to be stated here
that SHh can directly induce Snail (Wanshura et al., 2011). The role of Hh signal-
ling in EMT induction is also supported by reports that inhibitors of the pathway
do inhibit EMT activation (Gadgeel et al., 2011; Li et al., 2012d). Thomas et al.
(2011) found high levels of Gli1 expression in the triple-negative, highly invasive
breast cancer cell line, SUM149. Suppression of GLi1 by siRNA or Gli1 inhibitor
decreased cell proliferation and increased apoptosis and cell migration (
Figure 4.3
).




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search