Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Figures 3.4 and 3.5
The modulation of EMT and invasion/motility by miRNAs and the
signalling ligands and factors involved therein both upstream and downstream of miRNA
function. These two figures should read together. It should be borne in mind that EMT does lead
to the acquisition of invasive capacity. Here the depiction of c-met and invasion in two separate
illustrations is dictated merely by expediency. However, the routes of signalling differ markedly
for the different miRNAs. MiRNA-128a blocks the canonical TGF-β signalling cascade and could
effectively block EMT. MiRNA-194 has been reported to inhibit EMT by the downregulation
of the transcriptional repressor BMI-1, a PcG (Polycomb group) protein. Suppression of BMI-1
upregulates E-cadherin and downregulates Vimentin (this is not shown here).
these targets has been elucidated to a certain extent. There is nothing uncommon
with the three signalling pathways that are apparently involved in signalling by miR-
NAs. These are shown in
Figures 3.4-3.7
together with the miRNAs that are known
to activate and transduce the signals to their phenotypic conclusion. The numerical
abundance of miRNAs has inevitably led the investigations towards the well-estab-
lished signalling systems with precious little attention to cross talk between lines of
signal transduction and the function of the identified targets. These again represent
well-established molecular targets of which some are known to be able to transmit
signals downstream using different pathways and occasionally generating a diversity
of phenotypic outcome.

















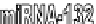















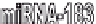





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search