Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 3.3
A chart of PTEN/Akt pathway in which PTEN inhibits Akt and promotes
apoptosis. Interacting with PTEN/Akt are JAK/STAT, MEK/ERK and mTOR pathways.
Fas receptor of the TNF receptor family upon being activated by binding of FasL induces
apoptosis. MiRNA-21 inhibits Fas/FasL and can also inhibit PTEN promoting cell
proliferation. Survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis, is believed to be suppressed by miRNA-708
leading to the promotion of apoptosis. The figure also shows how these signalling systems are
inhibited or mutually modulated by certain miRNA. References are provided in the text.
in two ways. Hypoxia induces many miRNAs, for example miRNAs-23, -24, -26,
-27, -103, -107, -181, -210 and -213; at least some of them via an HIF-1-dependent
mechanism (Kulshreshtha et al., 2007). HIF1-α activity is involved in the promotion
of angiogenesis by certain miRNA, for example miRNA-210. In some experimen-
tal systems such as MCF-7 breast cancer cells hypoxia induced an overexpression
of miRNA-210 and this was mediated by HIF-1α/VHL (Camps et al., 2008). The
authors also reported a negative correlation of disease-free and overall survival with
miRNA-210 levels. Hypoxia induces miRNA-424 in an HIF-dependent manner and
promotes angiogenesis (Ghosh et al., 2010). On the other hand, hypoxia has been
shown to be able to reduce the expression of miRNA-34a with promotion of EMT by
targeting Notch signalling (Du et al., 2012).
The ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloprotease) proteins are Zn-dependent met-
alloproteinases which release the extracellular domains of membrane-bound growth
factors, cytokines and their receptors. MMPs and ADAMs have similar domain
structure; they both possess a N-terminal propepetide region and a Zn catalytic
domain. MMPs have a C-terminal hemoplexin-like module. The ADAM proteins
possess a disintegrin domain C-terminal to the catalytic domain, then a cysteine-rich
domain and an EGF-repeat domain. ADAMTS has a TSP-1 (thrombospondin-like)
domain interposed between the disintegrin and cysteine-rich domains (Wee-Yong
et al., 2001; Paulissen et al., 2009).
ADAMs have been ascribed a potential role in angiogenesis being present in
endothelial cells. Inhibition of ADAMs inhibits endothelial cell migration and
adhesion
in vitro
. ADAM-17 has been shown to possess angiogenic property. It is










































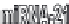























Search WWH ::

Custom Search