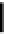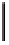Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
8
8
6
6
4
4
PLA
PLA
2
2
0
0
0
0
0.5
0.5
1
1
1.5
1.5
2
2
LTI content [phr]
LTI content [phr]
Fig. 16. Dependent of LTI content on the fracture energy,
J
in
.
(a)LTI: 0.5 phr
(b)LTI:1 phr (c)LTI:2phr
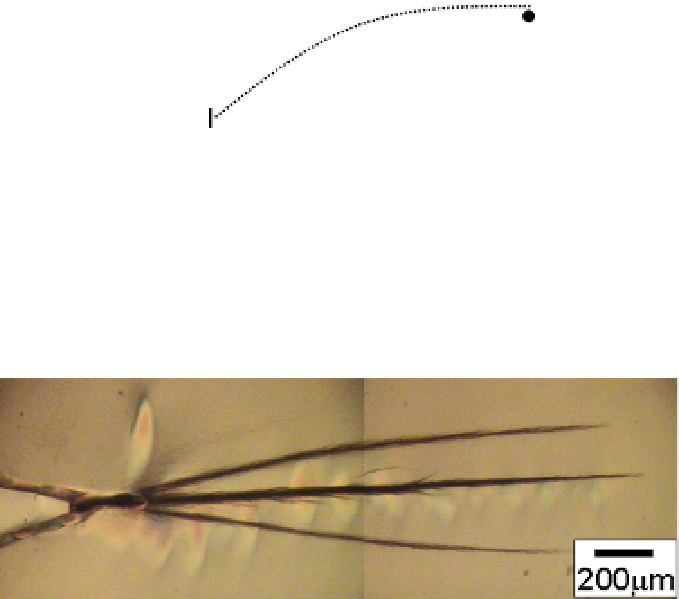
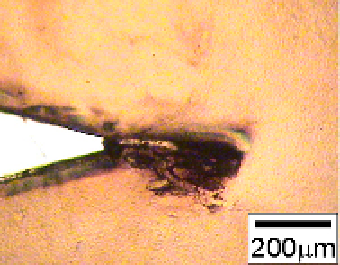
Fig. 17. Poralized micrographs of crack growth behaviors in PLA/PCL/LTI.
FE-SEM micrographs of fracture surfaces of PLA, PLA/PCL and PLA/PCL/LTI are shown
in Fig. 18. The fracture surface of PLA is very smooth, corresponding to a brittle fracture
behavior with low fracture energy. The surface roughness increases with the existence of
elongated PCL and cavities by PCL blending. These cavities are thought to be created by
debonding of the PCL-rich phases from the surrounding PLA matrix phase and usually
cause local stress concentration in the surrounding regions. Thus, this kind of cavitation
tends to lower the fracture energy because of the local stress concentration, and