Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3. Fibril formation of BC
To produce an elastic material from bio-inspired crosslinked BC gel (e-BC gel), heat
denaturation process is needed. By heat treatment, the cross-linked collagen fibrils shrink,
maintaining the cross-linkage among the collagen molecules and fibrils through the
denaturation of triple-helical collagen molecules to the random-coil form [24]. At the same
time, uncross-linked collagen molecules and fibrils may be lost through dissolution to water.
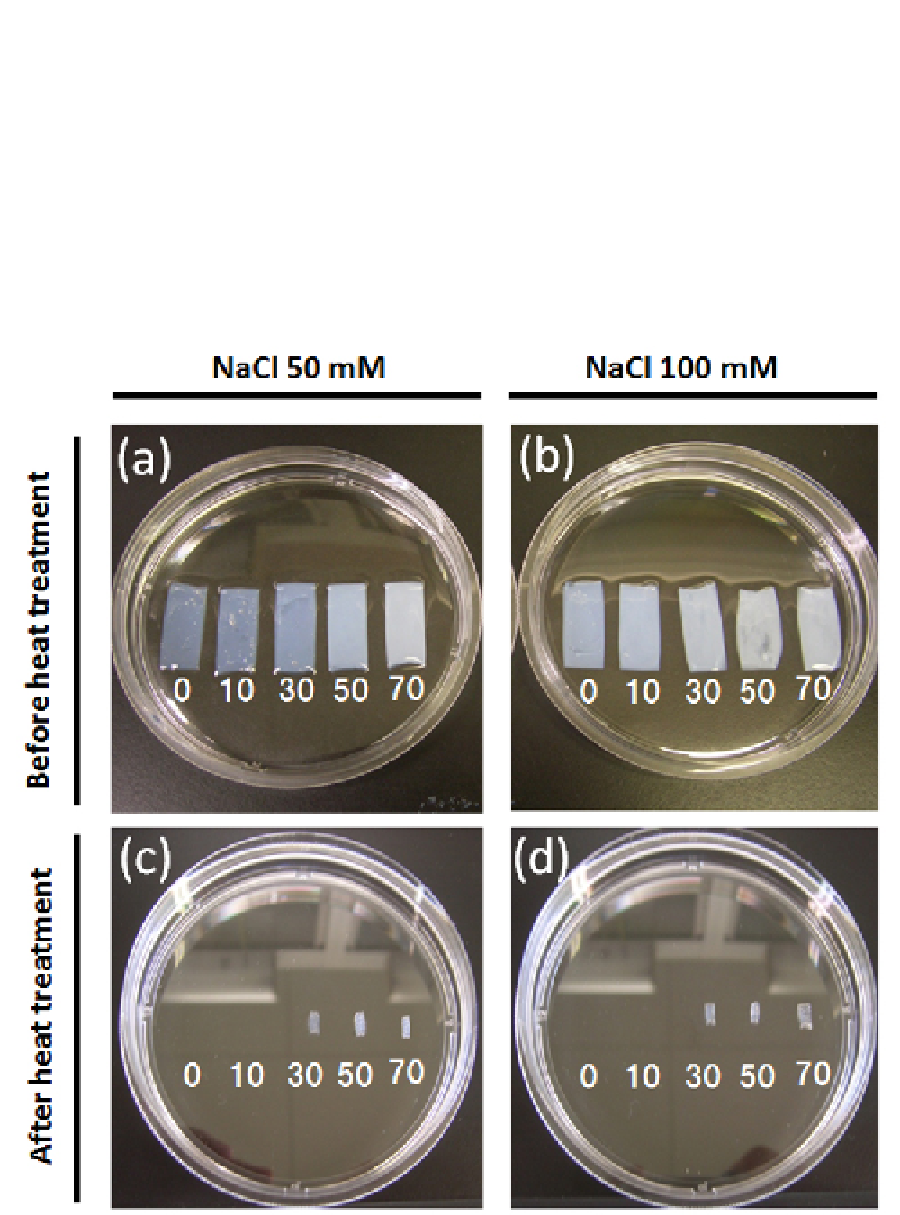
In fact, the original BC gels crosslinked with the EDC concentrations of 30-70 mM showed
drastic shrinkage (Fig. 5) and rubber-like elasticity after heat treatment at 60ºC for 5 min.
The BC gels crosslinked with EDC concentrations of 0-10 mM dissolved away after heat
treatment due to incomplete crosslinking.
Fig. 5. Appearances of BC gels (a, b) and e-BC gels (c, d). The values in the graphs indicate
the final EDC concentrations (mM) in the gels.