Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
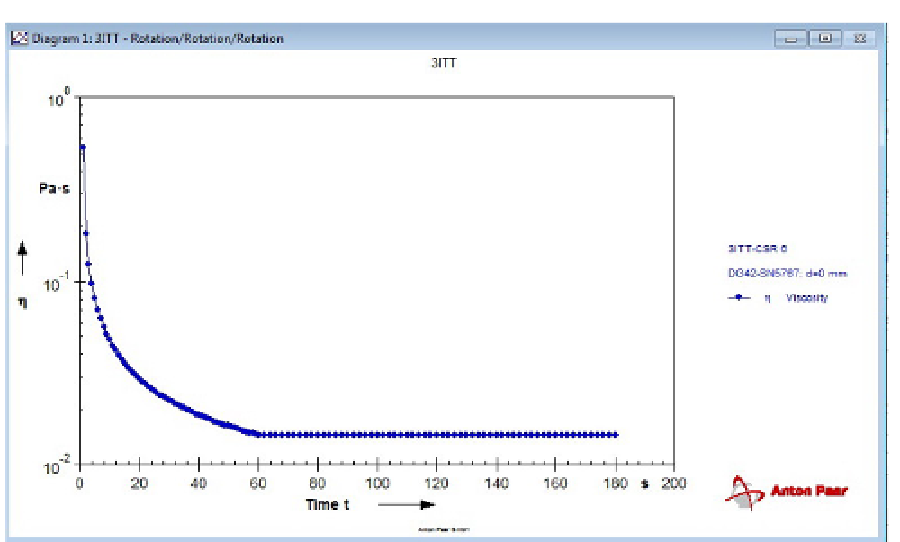
Fig. 7. Viscosity values of SF with increasing rate of flow velocity gradient 0 - 2000 s
-1
(in
time 0 - 60s) decrease. Viscosity values of SF are constant with constant rate of velocity
gradient 2000 s
-1
(in time 60 - 180s)
SF represents a mobile dispersion system in which
synovial gel is generated due to non-
Newtonian properties of SF.
Within this system, the macromolecules of hyaluronic acid can
be intertwined into a three-dimensional grid, which continuously penetrates through the
dispersion environment formed by water. The pseudoplastic properties of SF are manifested
through mechanical effects (for example while walking or running), Fig. 8., Fig. 9.
Physical
netting occurs, which is characterized by the interconnection of sections of polymer chains into knots
or knot areas.
Generally speaking, the association of individual molecules of hyaluronic acid
(HA/NaHA) occurs in cases of reduced affinity of its macromolecular chains to the solvent.
In other words, the
macromolecules of hyaluronic acid (HA) form a spatial grid structure in
a water solution
(Fig. 9.).
Mutually inverse shifts and inverse rotations of the opposite AC surfaces cause inverse
flows of SF on its interface with the AC surface (Fig. 10.).
The greatest magnitudes of SF velocity vectors due to the effect of shear stresses τ
xy
, (or the
effects of shifting forces respectively) are found near the upper and lower AC surface. They
are, however, mutually inversely oriented. Fig. 10. displays the right-oriented velocity
vector direction near the upper surface, and the left-oriented one near the lower AC surface.
The magnitudes of velocity vectors decrease in the direction towards the central SF zone. In
this thin neutral zone, the velocity vector is theoretically zero in value. A very thin layer
(zone) of SF in the vicinity of the central zone, with very small to zero velocities, can be
appointed
neutral SF zone.
At very small velocities of SF flows, the
viscosity of the neutral central zone is higher than the
viscosity in the vicinity of AC surfaces
. Under the conditions of very low viscosity, the SF
material in the vicinity of AC surfaces is characterized by a low friction coefficient. Friction
reaches values of ca 0.024 - 0.047 (Radin et al., 1971).