Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
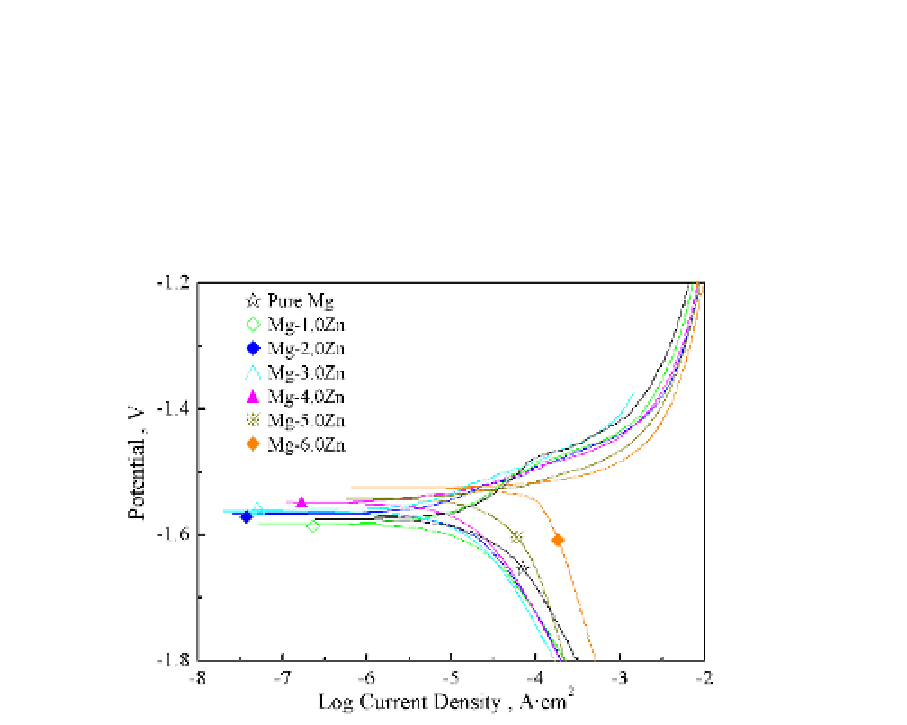
pure Mg was -1574mV. The corrosion potential was correlated with the Zn concentration.
The corrosion potential of Mg-2.0Zn and Mg-3.0 Zn alloys were about -1561 and -1568 mV,
respectively, which were nearly the same and about 10 mV high than that of pure Mg. The
Mg-5.0 Zn and Mg-6.0 Zn alloy samples exhibit high corrosion potentials of about -1524 and
-1547 mV, respectively, which were about 50 mV higher than that of pure Mg. It could be
seen that the addition of Zn improved the corrosion potential of the as-cast Mg-x Zn alloys.
But, the addition of elements Zn was also increased the current densities of the resulted as-
cast Mg alloys in Hank's solution.
Fig. 8. Potentiodynamic polarization curves of Mg-Zn alloys in SBF solution
The reason for the increase corrosion potential of Mg-x Zn alloys was that the Zn element had
a high electronegative. But, when the Zn concentration increased, the corrosion resistance was
decreased. The reason for the reduced corrosion resistance of Mg-x Zn alloys was that the
second phase precipitated during the solid solidification processes, which accelerated the
corrosion rate due to the different electrochemical behaviors of α-Mg and precipitates.
Generally, the cathodic polarization curves were assumed to represent the cathodic
hydrogen evolution through water reduction, while the anodic polarization curves
represented the dissolution of magnesium. It could be seen that the cathodic polarization
current of hydrogen evolution reaction on Mg-1.0 Zn alloy sample was much lower than
that of Mg-5.0 Zn and Mg-6.0 Zn Ca alloys sample, suggesting that over potential of the
cathodic hydrogen evolution reaction was lower for Mg-1.0 Zn and Mg-2.0 Zn alloys
sample. As a result, the cathodic reaction was kinetically more difficult on the Mg-1.0 Zn
alloy and Mg-2.0 Zn alloy sample than that on the Mg-5.0 Zn Ca alloy samples. The
degradation rates of Mg-1.0Zn degraded were slower thanMg-5.0Zn, Mg-6.0Zn, which was
adherence to the electrochemical results.
3.3.2 The effects of Ca content on in-vitro degradation of the as-cast Mg-Zn-Ca alloys
The representative potentiodynamic polarization curves of the pure Mg and Mg-4.0 Zn-x Ca
alloys in Hank's solution were shown in Fig.9. The mean corrosion potentials of Mg-4.0Zn-