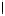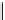Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3.3.2 Statistical analysis
Because of the numerous variables studied pertaining to the ability of this adsorbent to
remove each of these metal ions from a flowing influent, it became imperative that statistical
tools be employed to ascertain differences (and similarities) in metal binding. Variables that
were tested include the esterification of carboxylate functionalities, the identity of the metal
bond, the identity of the metal ion(s) displaced or removed, and the general history of a
column of the biosorbent. The Student-t test was employed to test the hypothesis that the
measured means of binding capacities between any two conditions were statistically the
same. The criteria used for these test were a 95% confidence level with 2 - 5 degrees of
freedom.
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Cd1st
Cd2nd Cd3rd
Ni1st
Ni2nd
Ni3rd
Zn1st
Zn2nd
Zn3rd
Metal & Position
Fig. 4. Comparison of native (shaded) and modified
D. innoxia
columns influent-metal
bound capacities. Metal bound is reported in micromoles per gram biomaterial.
To statistically treat the results presented above in the comparison of the native and
esterified biomaterial, two methods of statistical analysis were used. The Student-t test was
used to test the statistical difference between the amounts of metal bound to the biomaterial
at each stage in the studies at each stage for the native and modified biomaterials. This
would also reinforce the position that by undertaking a simple chemical modification, the
binding properties of a biomaterial could be altered significantly. Also, the Student-t test
was used to examine the impact of exposure order and history (e.g., whether the amount of
cadmium bound to the biomaterial is statistically different for the series Ni
2+
Zn
2+
Cd
2+
and Zn
2+
Ni
2+
Cd
2+
). Differences in the variances calculated for each stage were
similarly evaluated using an F-test (again considering both the order of metal ion exposure
and the exposure history of the material).
Table 3 summarizes the resulting statistical comparisons of the native and chemically
modified
D. innoxia
materials using the software package 'Analysis ToolPak' within
Microsoft® Excel™. Mass balance values of the influent metal bound were used in these