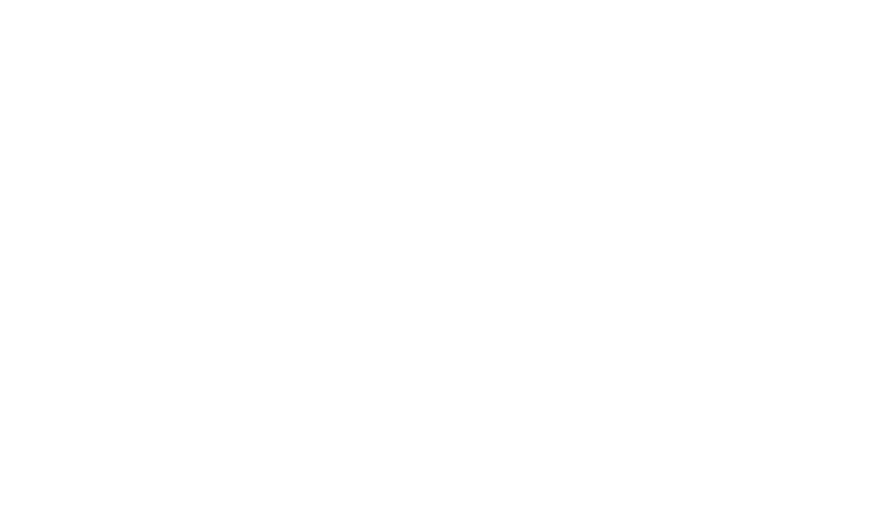Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
extract chemical information by careful decomposition of the peaks. This requires to impose
reasonable constraints (number of components, full width at half maximum FWHM) in
order to insure reliable comparisons, and to check the chemical relevance of the results by
examining correlations between spectral data of different natures (Genet et al., 2008;
Rouxhet & Genet, 2011). In previous studies (Landoulsi et al., 2008a; Landoulsi et al., 2008b),
we have demonstrated the usefulness of this approach, even when the evolution of the C 1s
and O 1s peak shape is weak, in order to obtain information on the amount and the nature
of organic and inorganic constituents on SS surfaces.
O 1s
O 1s
O 1s
C 1s
C 1s
C 1s
sil+BS+Gox
sil+BS+Gox
sil+BS+Gox
sil+Gox
sil+Gox
sil+Gox
sil+BS
sil+BS
sil+BS
sil
sil
sil
nat
nat
nat
538 536 534 532 530 528 526
538 536 534 532 530 528 526
538 536 534 532 530 528 526
294 292 290 288 286 284 282 280
294 292 290 288 286 284 282 280
294 292 290 288 286 284 282 280
5
3
8
538
538
5
3
6
536
536
5
3
4
534
534
5
3
2
532
532
5
3
0
530
530
5
2
8
528
528
5
2
6
526
526
2
9
4 2
9
2 2
9
0 2
8
8 2
8
6 2
8
4 2
8
2 2
8
0
Bin din g En erg y (e V)
294 292 290 288 286 284 282 280
Bin din g En erg y (e V)
294 292 290 288 286 284 282 280
Bin din g En erg y (e V)
Bin din g En erg y (e V)
Bin din g En erg y (e V)
Bin din g En erg y (e V)
Binding Energy (eV)
Binding Energy (eV)
Binding Energy (eV)
Binding Energy (eV)
Binding Energy (eV)
Binding Energy (eV)
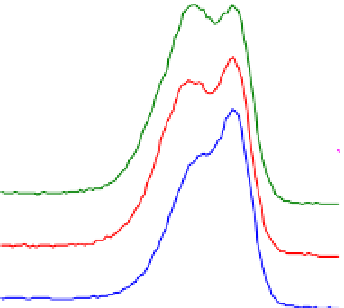
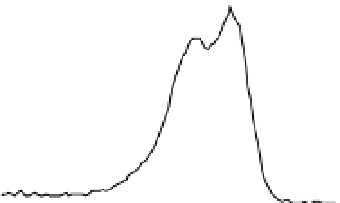
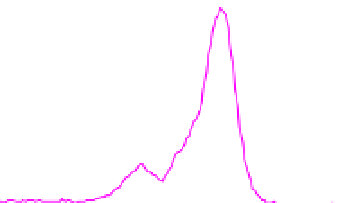
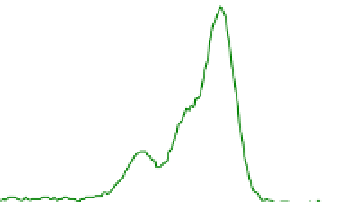
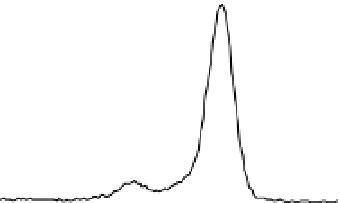
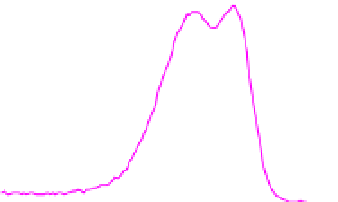
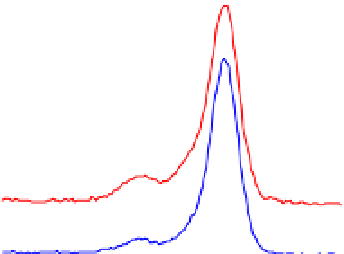
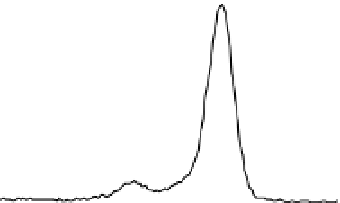
Fig. 2. O 1s and C 1s peaks of native (nat), of silanized stainless steel (sil), of the same after
treatment with the coupling agent (sil+BS), after adsorption of glucose oxidase (sil+Gox)
and after treatment with glucose oxidase subsequent to treatment with the coupling agent
(sil+BS+Gox).
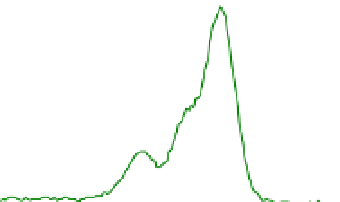
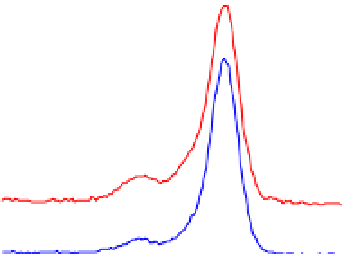
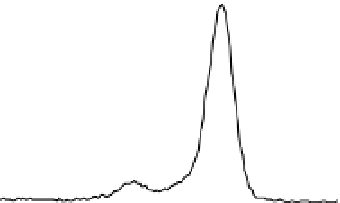
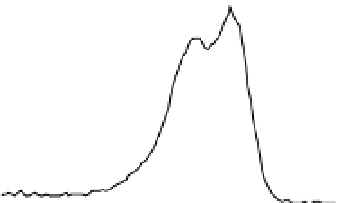
Figure 3 presents typical O 1s, N 1s and C 1s XPS peaks recorded on native SS (nat),
silanized (sil) and the same after Gox treatment (sil+Gox). For the decomposition of these
peaks, reasonable constraints were applied, based on our experience with the XPS analysis
of biosurfaces (Genet et al., 2008, Rouxhet & Genet, 2011). The C ls peak was decomposed in
four components, the FWHM of which were imposed to be equal: (i) a component at 284.8
eV due to carbon only bound to carbon and/or hydrogen [C-(C,H)]; (ii) a component at
about 286.3 eV due to carbon making a single bond with oxygen and/or nitrogen [C-(O,N)]
in alcohol, amine, or amide; (iii) a component at 287.8 eV due to carbon making one double
bond or two single bonds with oxygen (C=O, O-C-O) and (iv) a component at 288.7 eV
attributed to carboxyl or ester functions [(C=O)-O-R].