Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The uncomplete crosslinking of Ulvan macromers under UV exposure could be ascribed to
both the nature and the morphology assumed by this polysaccharide in solution. Indeed the
antioxidant activity of Ulvan could reduce the rate of radical polymerization of the
macromers by quenching the radicals formed during the UV irradiation. Moreover the
aggregative behaviour of Ulvan in aqueous solution reduces the amount of (meth)acryloyl
groups available for polymerization thus partially inhibiting the crosslinking.
The property of retaining water represents a key parameter for evaluating the quality of a
hydrogel and its potential use for biomedical applications because it usually affects its
permeability, biocompatibility and rate of degradation. The swelling ability of hydrogels
could also provide information about their mechanical stability and chemical and physical
properties, since the degree of water uptake is related both to the chemical nature and to the
physical structure of the polymeric network (Qi et al., 2004). It is known, for example, that
gels exhibiting a larger pore structure - likely due to a lower degree of crosslinking - have
poor mechanical strength and higher swelling ratios (Anseth et al., 1996).
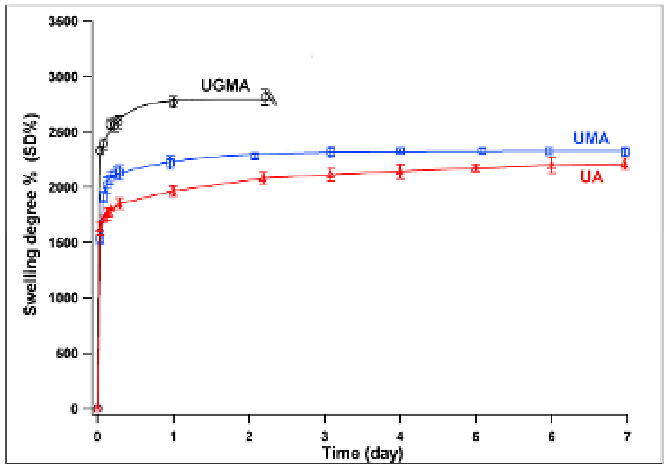
The swelling ability of hydrogels is usually quantified by measuring their Swelling Degree
% (SD%) taken as the ratio (%) between the weight of the swollen hydrogel to that of the
dried sample. The swelling degrees of the prepared Ulvan hydrogels have been carried out
in phosphate buffer solutions (pH 7.4) and their behaviour was recorded during 7 days of
immersion (Fig. 10).
Fig. 10. SD% in PBS buffer solution (0.1 M, pH 7.4) of UV crosslinked (365 nm,
approximately 8 mW· cm
-2
) UMA and UGMA hydrogels as a function of time.
Pictures of the swollen scaffolds taken after 2 days of immersion in phosphate buffer saline
(PBS) at pH 7.4, showed that the Ulvan methacrylate (UMA) hydrogels proved to be most
stable in terms of texture and mechanical properties (Figure. 11).
The swelling degree experiments of UGMA-based samples were stopped after 2 days of
immersion since the hydrogels were no longer coherent and hence not easy to handle. This