Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
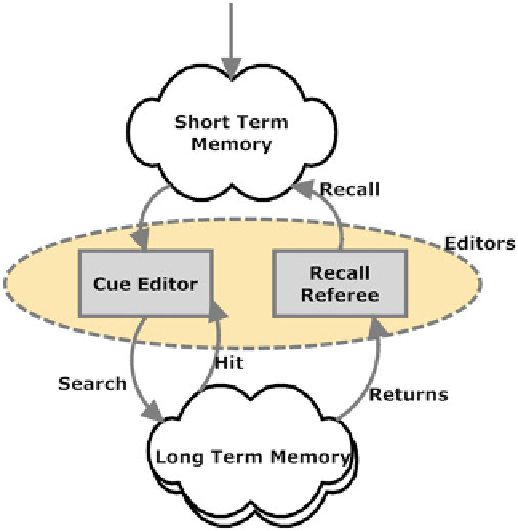
Fig. 2.2
Subliminal editors in relation to short- and long-term memories
without being noticed, adding or subtracting cues from a search until the cues are
exactly right, as they must be for a recall.
A cue editor helps resolve conflicting cues (which would result in no matches in
long-term associative memory). The term hit in the above figure means that a return
has occurred. But if hit is false, it is the task of the cue editor to modify the cues
slightly so as to produce a return. As new images from the senses appear in STM,
new rounds of cue editing are necessary. The past unfinished editing process moves
into the background but keeps working. This is why a person sometimes belatedly
recalls a forgotten piece of information. A subsequent chapter goes into circuitry for
a cue editor.
A cue editor is not in a position to judge the priority of multiple returns. This is
the task of a recall referee.
Recall Referee
An underdetermined set of cues generally results in a plethora of returns (think of
everything you know that contains the color green, for instance). This overabun-
dance has to be processed to assess the priority of each. If something is critical, it
must be passed quickly into STM, because survival may be involved. For instance,
safe responses in the event of danger must be promptly directed into conscious STM.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search