Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
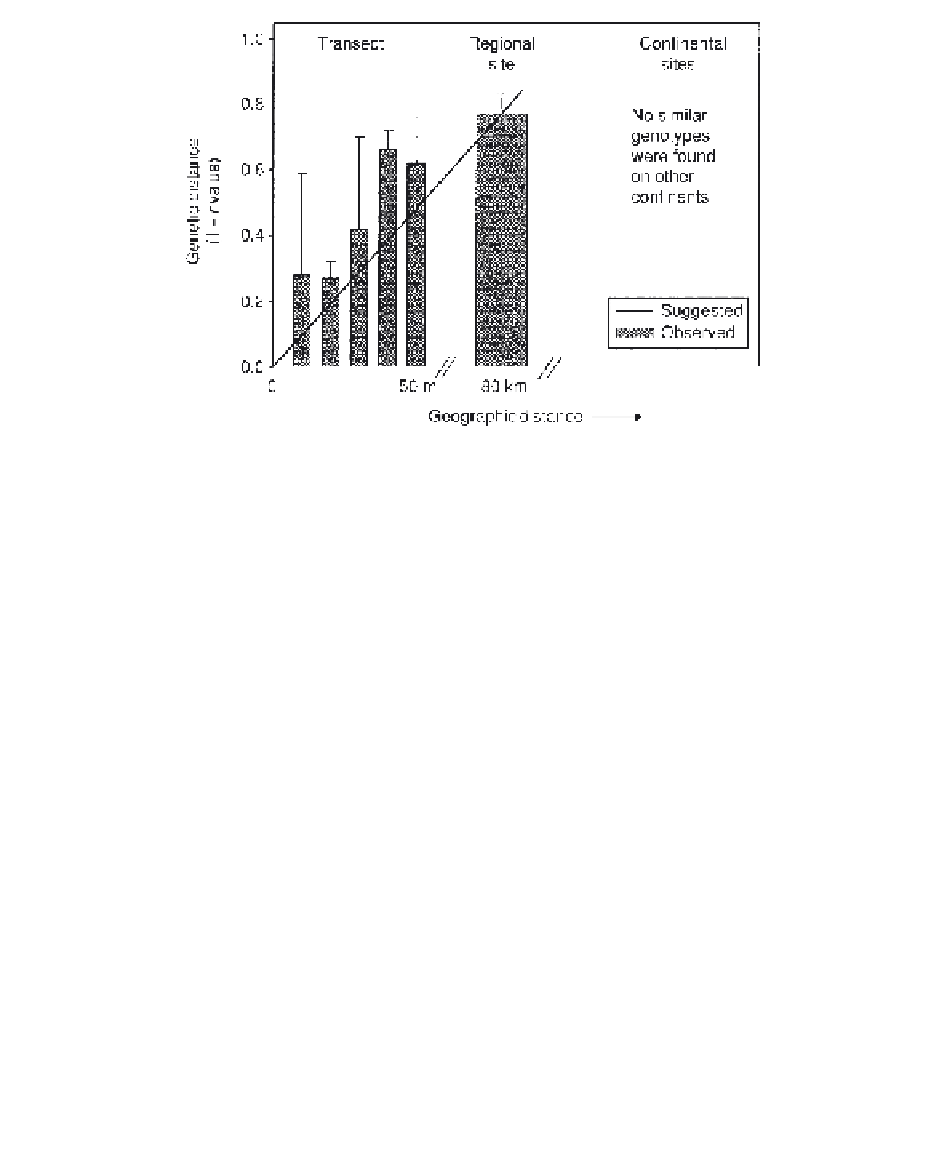
Fig. 6.4.
The relationship between genetic distance based on genomic fingerprinting (rep-PCR)
and geographic distance between isolate sources. The method does not resolve large genetic
distances well but does confirm that similar genotypes were not isolated at other sites in the region
or on other continents.
base and calculated similarity coefficients to every other genotype in the
transect, to all transect isolates of a second Australian site and to all transect
isolates in different regions. Those values plotted against geographic
distance revealed a relationship of increasing diversity with distance. The
methodology we have used so far provides its best resolution at transect
scale genetic differences. We currently are working to obtain additional
measures that will allow this relationship to be evaluated at larger
geographic scales. While these findings support the endemism hypothesis,
they also suggest that the resulting corollary is true, i.e. that bacterial
diversification is actively ongoing.
Applications of DNA Microarray Technology to
Environmental Microbiology
Introduction to microarray technology
Since the advent of microbial genome sequencing programmes less than
8 years ago, a massive amount of microbial genome sequence information
has been collected. The complete sequences for > 20 microbial genomes
have been determined, and > 100 microbial genome sequencing projects
are now in progress (www.tigr.org). The next step in the era of microbial

































Search WWH ::

Custom Search