Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
catabolic evenness did indeed indicate that these soils were under stress, as
the organic C pools were similarly depleted (Table 5.1.1). Catabolic even-
ness may be an integrative indicator of biological condition that does not
require parallel measurements on reference land uses in order to be inter-
pretable. The absolute value of the catabolic evenness for a soil has the
advantage in being readily judged as favourable or unfavourable, unlike
other indicators of biological condition, which cannot be evaluated in
isolation.
Relationships Between Microbial Catabolic Evenness
and Organic C
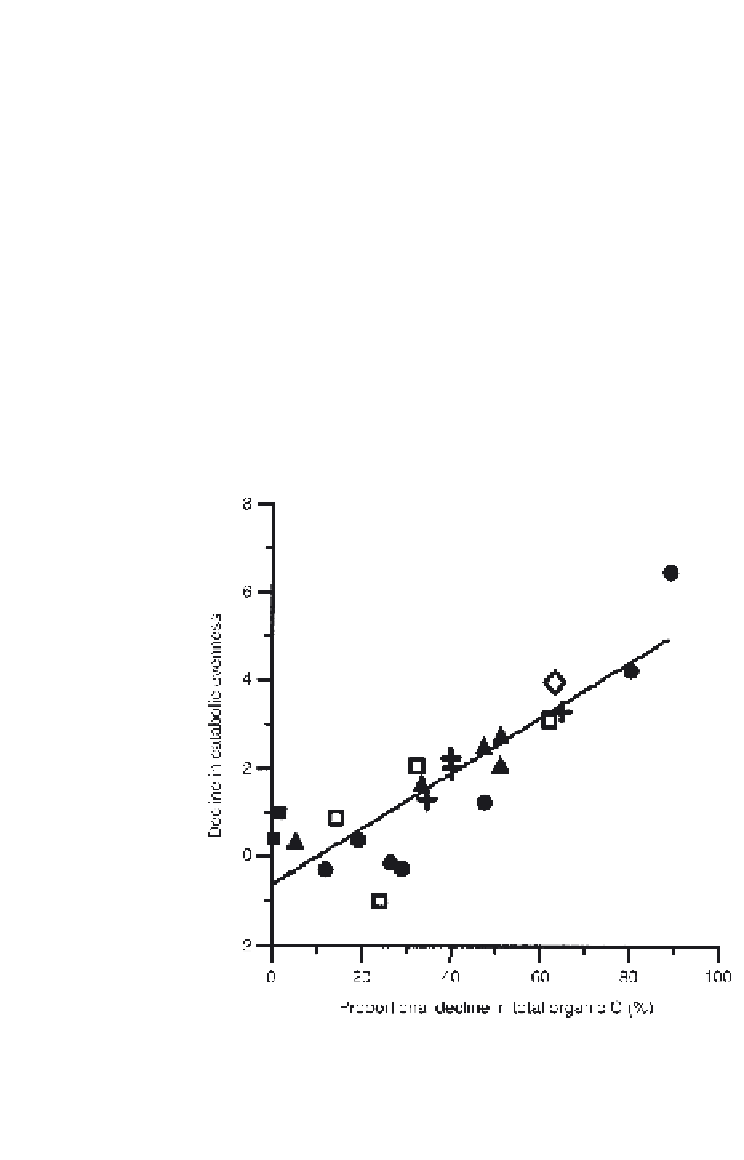
Loss of catabolic evenness of soils can be linked with losses in soil organic
matter. Only weak generalized relationships exist between organic C pools
in soils and microbial catabolic evenness that can be applied across soil
types (Degens
et al
., 2000b). However, comparisons of long-term cropping,
Fig. 5.1.1.
Proportional decline in total organic C in relation to declines in catabolic evenness
for comparisons between pasture and other land uses across a range of soil types (r
2
= 0.76;
P< 0.01). Pasture was paired with pine forest (
r
, Pi), indigenous vegetation (
w
, N), cropping
(
✚
, C), chemical fallow (
{
, CF), mixed cropping (
x
, MC), or effluent-treated pasture (
v
, PE).
After Degens et al. (2000b).










Search WWH ::

Custom Search