Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
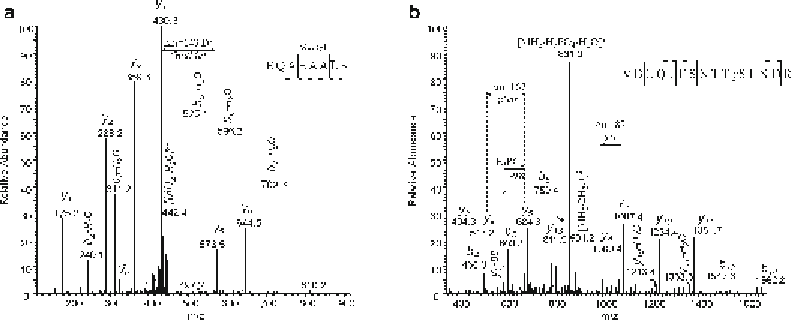
Fig. 2
Manual verifi cation of posttranslational modifi cations, identifi ed by Mascot. (
a
) Methylation of glutamic
acid. Mascot reported a peptide sequence with low mass error (<5 ppm) originating from the viral proteome
and a methylation on aspartic or glutamic acid (Methylation (D, E)) as modifi cation. The theoretical backbone
cleavage was clearly observed (normally with signal/noise (S/N) >3). In this example ion y
5
has high S/N ratio
and identifi es methylated glutamic acid in position 4. Mass difference between y
4
and y
5
ions equals 143 Da
(Glutamic acid (Glu) +14, i.e., CH
2
for methylation). Position 1 lacks methylation, that is confi rmed by the loss
of H
2
O molecule from carboxylic group of b
2
ion (COOCH
3
cannot lose H
2
O molecule), as well as by b
2
ion mass
of 240.1 Da (Glu-H
2
O+Gln+1). (
b
) Phosphorylation. Similarly to methylation, pairs of y
4
and y
5
ions with S/N > 3
and mass difference of 167 Da identify phosphoserine in position 11. Observed neutral loss of 98 Da (phos-
phoric acid) from y
5
ion confi rms that serine 11 is phosphorylated. Additional evidence is a clear mass differ-
ence of 87 Da (unmodifi ed serine) between y
8
and y
9
ions, i.e., serine 7 is not phosphorylated. Exact mass of
this peptide indicates the presence of only one phosphorylation. Therefore the phosphorylation at serine 11 is
confi rmed by manual verifi cation
4
Notes
1. All reagents to be used for sample preparation for MS analysis
should have purity specifi ed for LC-MS application and water
used should be so-called Milli-Q water. Sterile solutions are
required during the virus production steps. We strongly rec-
ommend processing all samples from the designed study using
chemicals and plastic material from the same batch in order to
avoid “batch effects” [
36
].
2. The detectability of different proteins in a virus particle will
vary depending on a number of parameters. In Table
1
we have
summarized the characteristics and the results obtained for
analysis of Adenovirus type 2 using mass spectrometry. The
number of copies of a certain protein per virion will refl ect the
abundance of peptides originated from this protein in the sample.
For example in adenovirus type 2 the hexon protein is domi-
nating in the virus particle, and peptides of the hexon protein