Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
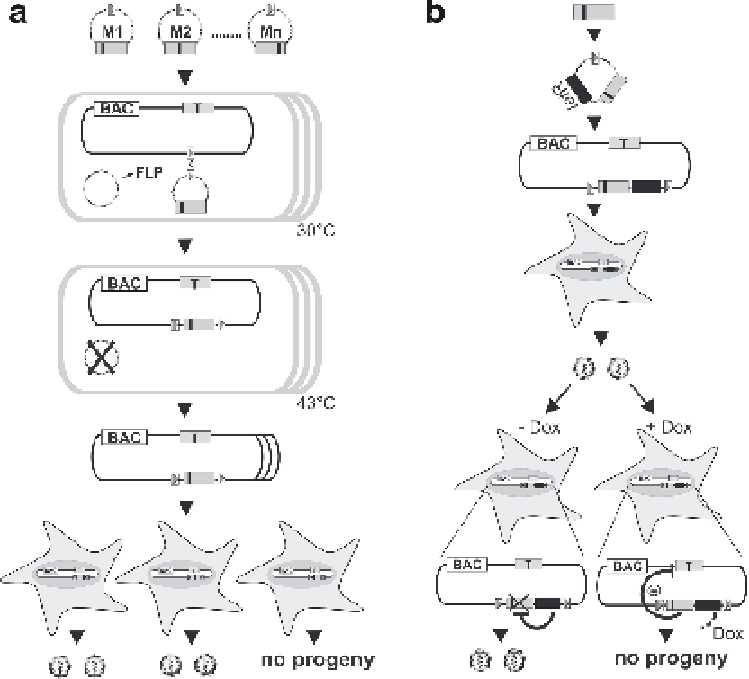
Fig. 7
Screening for and characterization of dominant-negative mutants of essential viral genes.
a
Screening for inhibitory mutants. An essential viral gene, the target gene (
gray box, T
), is sub-
cloned and subjected to a random and comprehensive mutagenesis in vitro leading to a mutant
library M1, M2, . . . Mn (
small black boxes
indicate mutations). Mutated ORFs are placed under
the control of a strong constitutive promoter into an insertion plasmid containing an FRT site (
open
box with gray triangle
). The insertion plasmids can only be maintained in a special
E. coli
strain.
Normal
E. coli
(
open boxes
) carrying an FRT site-labeled viral bacterial artificial chromosome
(
BAC
) and a temperature-sensitive plasmid-expressing FLP recombinase (
FLP
) are transformed
with the insertion plasmids carrying different mutants one by one. The FLP recombinase mediates
site-specific recombination between the FRT sites in the BAC and the insertion plasmids. This
recombinants can then be isolated under combined antibiotic selection for both the BACs and the
insertion plasmid. The FLP-expressing helper plasmid is removed by elevated temperature. Then
BAC DNA is prepared and permissive cells are transfected with each construct. The mutants that
are able to inhibit the virus reconstitution can be selected on the basis of the inability of plaque
formation upon transfection.
b
Validation of dominant negative mutants by conditional gene expres-
sion. The inhibitory mutants are subcloned under the control of a promoter regulated by the TetR
(
black box
) into an insertion plasmid with an FRT site. These constructs are delivered into the viral
BAC as described above. Then permissive cells are transfected with the recombinants in order to
reconstitute viruses carrying the regulation cassettes for the inhibitory mutants. The inhibitory mutants
are not expressed during reconstitution because in the absence of doxycycline (
- Dox
), the consti-
tutively expressed TetR blocks their transcription. The inhibitory function of the mutants can be
analyzed upon doxycycline administration (
+ Dox
), which leads to the expression of the inhibitory
mutant by releasing the expression cassette from the TetR regulation