Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
not necessarily coupled with the splicing reaction (Strasser and Hurt 2001). Indeed,
several studies showed that UAP56 recruitment to the mRNA can also occur via
co-transcriptional mechanisms (Zenklusen et al. 2002; Kiesler et al. 2002; Strasser
et al. 2002). Furthermore, while REF proteins were found to be dispensable for bulk
mRNA export, inactivation of UAP56 leads to a nuclear retention of poly(A) mRNA,
indicating that this protein plays a central role for mRNA export (Gatfield and
Izaurralde 2002; Gatfield et al. 2001; Kapadia et al. 2006).
Interaction of the Human Cytomegalovirus Protein pUL69 with
the mRNA Export Factor UAP56
The human cytomegalovirus protein encoded by the open reading frame UL69
belongs to a family of regulatory factors that is conserved among all herpesviruses
and includes the proteins ICP27 of herpes simplex type I (HSVI), EB2 of Epstein-
Barr virus (EBV), and the ORFs 57 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
(KSHV) and of Herpesvirus saimiri (HVS) (for reviews see Lischka and Stamminger
2006; Sandri-Goldin 2004; Sandri-Goldin 2001). Although the amino acid identity
among these proteins is not very high, ranging from 17% to 36%, they share a
region showing a higher conservation of approximately 40% sequence identity.
This conserved region can be found at the C-terminus of the α- and γ-herpesvirus
proteins, whereas it corresponds to the central part of the β-herpesviral proteins
since they have a unique C-terminal domain (Winkler et al. 2000) (see Fig. 3).
Recently, we demonstrated that this homology region folds into a globular core
domain according to secondary structure predictions and is responsible for a shared
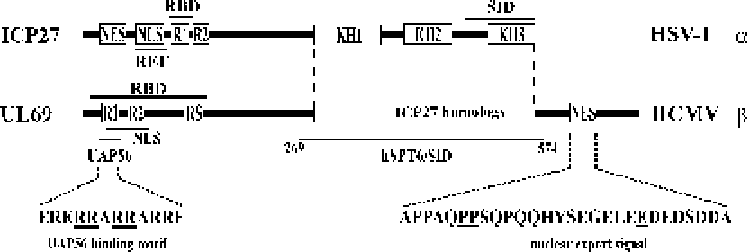
Fig. 3
Domain organization of the HCMV UL69 protein in comparison to the HSV-1 protein
ICP27 showing the positions of important functional regions. The sequence of the UAP56-binding
motif within pUL69 is depicted, as is the sequence of the leptomycin B-insensitive NES; under-
lined amino acid residues are critical for the function of the respective motifs.
NES
nuclear export
signal,
NLS
nuclear localization signal,
R1
,
R2
,
RS
arginine-rich regions,
RBD
RNA-binding
domain,
KH1-3
putative KH RNA-binding motifs,
ICP27 homology
domain of pUL69 with high
homology to ICP27,
SID
self-interaction domain,
REF
UAP56,
hSPT6
binding sites of the
respective cellular factors