Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Two major types of wetlands could be differentiated, based on the hydraulic
conditions - free water system and submerged flow system wetlands. The free water
system wetlands are basins or wide channels, which provide for a flow with a free surface
among the grown vegetation and direct the flow movements. Their bottom is covered
with impervious cover to prevent seepage to the ground water. Part of the basins and
channel volumes are filled with soil to provide the basis for emerging vegetation.
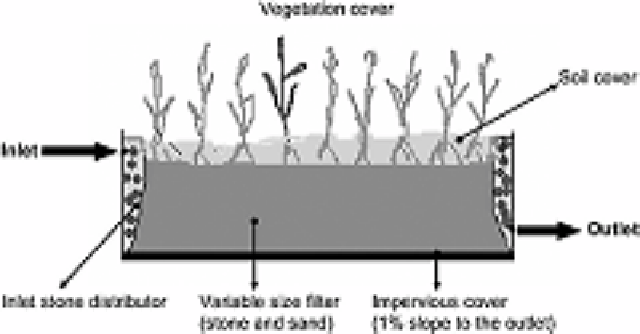
Submerged flow systems, known also as “constructed” wetlands, do not provide for free
flow. A schematic representation is shown in Figure 2.6.
Wetlands are widely used options for treatment of polluted runoff at a large and at a
small scale in on-site units. Large-scale wetlands are incorporated into the landscape
design of the area and could form part of parks and recreational areas. It is
recommendable to incorporate a pre-treatment facility for coarse and heavy particles
removal before the wetland inlet, in order to avoid the accumulation of sludge and
clogging. The design of a wetland system requires profound knowledge of the hydrology
of the site, especially when the runoff water is the only source to feed and maintain the
wetland. Care should be taken to provide for minimum water requirements throughout
the year. If water is not supplied regularly and there are considerable periods of dry
spells, the wetland might be lost. Wetlands require little operation and maintenance
efforts, but should be regularly inspected to ensure that there is no disruption of the flow
due to sediments deposition or vegetation overgrowth. Periodical cleaning and vegetation
clearance would also be necessary.
Figure 2.6. Schematic representation of
a subsurface (constructed) wetland
system.
3.3.4
Filters
Sand filters could be used as a polishing step for polluted runoff treatment. They have
been applied mainly for small on site units or elements of the drainage system. Sand
filtration removes pollutants based on adsorption and absorption processes. Filters