Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
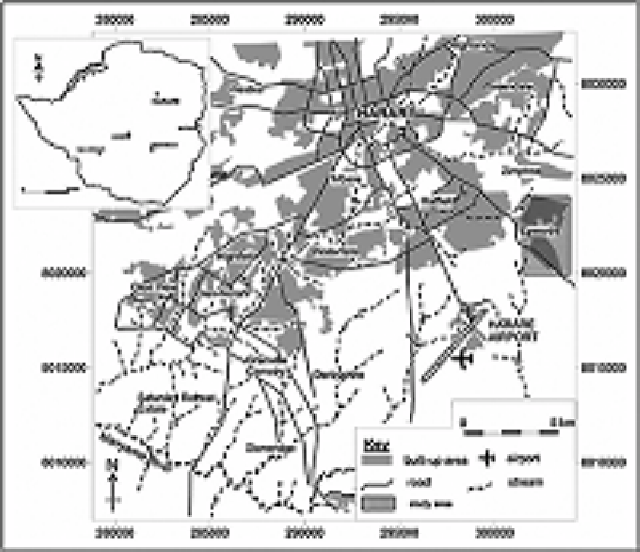
Figure 6.2. Location of Epworth.
An elected Local Board was established under the Urban Councils Act (1992) to manage
the affairs of the settlement. The Epworth Local Board gets grants from the central
government for infrastructure development and it also collects rates from residents in the
serviced areas. The settlement now comprises five administrative sections of Maguta,
Makomo, Zinyengerere, Chinamano and Overspill villages (Fig. 6.3). Each of these
sections has an extension village.
Settlement patterns vary across different villages, with some exhibiting more regular
patterns and others being characterized by haphazard patterns. Each village has both
formal settlements and informal “gada” settlements. Gada residents occupy untenured,
unserviced and low-lying or otherwise unattractive land. The “gadas” are considered to
be informal settlements by the Epworth Local Board. The overall character of Epworth is
thus a semi-formal or mixed formal/informal settlement. An illustration of such type of
residential development is shown on Figure 6.4. Note the small dwelling sizes, pit latrine
outhouses and the dambo (wetland) in the foreground.
1.4
Objectives of this study
This study was undertaken to determine the impact that the Epworth semi-formal
settlement has on groundwater quality, and the implications for the settlement's water
supply. It was carried out via two activities: a water supply and sanitation survey (to
determine how residents obtain domestic water and how sewage is disposed of) and a