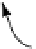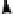Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
7
6
Figure 4.3
Optimum pH for soil
nitrifiers (redrawn from
White 1997).
5
5
6
7
8
Soil pH
that the optimum pH for nitrification is close to the soil pH (fig. 4.3).
Thus, the optimum pH in any soil is unlikely to exceed 6.6-6.8.
• Autotrophic nitrifiers are strict aerobes. Once the O
2
partial pressure in the
soil air falls below 0.4 kPa, nitrification ceases. Under these conditions,
reduction of NO
3
or
denitrification
may occur (section 5.6.1).
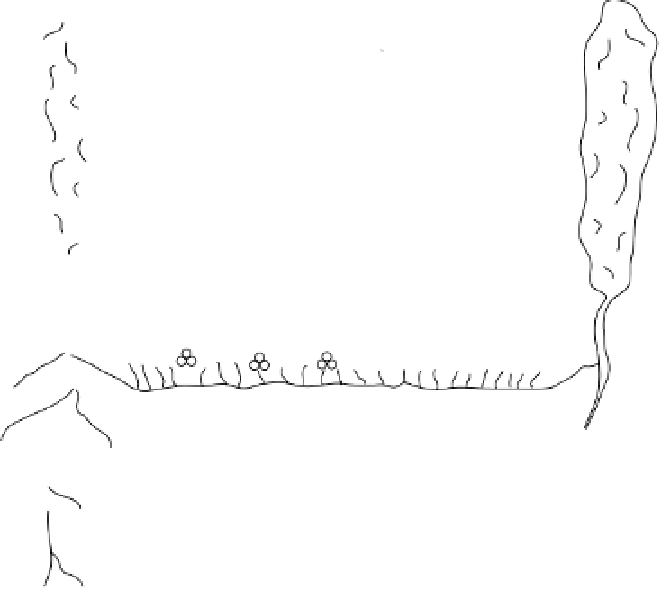
Ammonification, nitrification, and immobilization are key processes in the
overall cycling of N among the atmosphere, soil, and plants, called the
nitrogen
cycle
(fig. 4.4).
Vine row
NH
4
+
and NO
3
-
from
Leaf fall,
prunings
atmosphere, fertilizers
N
2
fixation
Volatilization
Cover crop (with clover)
NH
3
NH
4
+
Organic N
fertilizers
Immobilization
Ammonification
NH
4
+
N
2
Nitrification
3
-
N
2
O
NO
Uptake
Denitrification
Leaching
N cycle in a vineyard soil system.
Figure 4.4