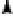Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
solution concentration. As discussed in chapter 3, the expansion or contraction of
DDL
s at clay surfaces is crucial in determining whether clay crystals remain floc-
culated. Further, the state of clay flocculation strongly influences the stability
of soil aggregates and the soil's structure in general, a topic taken up again in
chapter 7.
4.5.3
Some Additional Effects on the DDL
All ions in solution are hydrated. The radius of a hydrated ion is larger than that
of an unhydrated ion. We saw in box 2.6 that, under the polarizing effect of fixed
charges in a mineral surface, cations could either completely dehydrate to form
tightly bound complexes with the surface or partially dehydrate to form less tightly
bound complexes. In both cases, the cation is pulled close to the surface, effec-
tively moving from the diffuse part of the
DDL
into a layer called the Stern layer
immediately adjacent to the surface (fig. 4.7). This process is called
specific ad-
sorption
. Specific adsorption forces add to the
nonspecific
electrostatic forces de-
scribed previously. Overall, specific forces acting on the cations cause the
DDL
to
become more compressed. For cations of the same valency, such as the series Li
,
Na
, K
, Rb
, and Cs
, the ease of dehydration of the cation increases as the
atomic radius increases, from Li
through Cs
. Consequently, the specific ad-
sorption effect increases with the size of the unhydrated cation, and we find that
Cs
, for example, is much more strongly adsorbed than Na
. The
DDL
of a Cs-
saturated clay is more compressed than that of a Na-saturated clay, and hence Cs-
clays flocculate much more readily than Na-clays.
4.5.4
Anions and Charged Surfaces
Anions such as Cl
, SO
4
2
and HCO
3
are normally repelled from negatively
charged surfaces. However, if an anion has a strong chemical affinity for metal
Figure 4.7
Diagram of a diffuse double
layer at a negatively charged clay
surface showing Stern layer
cations (after White 1997).
Stern layer cation
Total
surface
electrical
potential
Inner region of diffuse layer
Diffuse
layer
Diffuse layer
potential
Stern layer
0
Distance, x