Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
(Woodroffe 1990). They specifically favour tidal shore-
lines with low wave energy, and in particular brackish
waters of estuaries and deltas (Figure 13.19). Some man-
grove species are tolerant of more frequent flooding than
salt marsh species, and so mangals extend from around
the high spring-tide level to a little above mean sea level.
They often contain
lagoons
and pools, but not the pans
of salt marshes. Like salt marshes, mangals have creek sys-
tems, although their banks are often formed of tree roots.
Marine deltas
Marine deltas are formed by deposition where rivers run
into the sea. So long as the deposition rate surpasses
the erosion rate, a delta will grow. Deltas are found in
a range of coastal environments. Some deltas form along
low-energy coasts with low tidal ranges and weak waves.
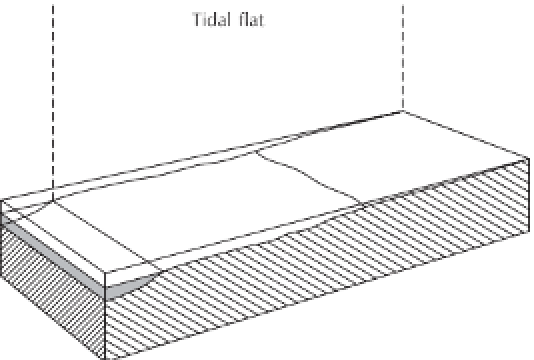
Figure 13.18
Tidal flats and their morphological units
based on low- and high-tide positions.
Source:
Adapted from Davies (1980, 170)
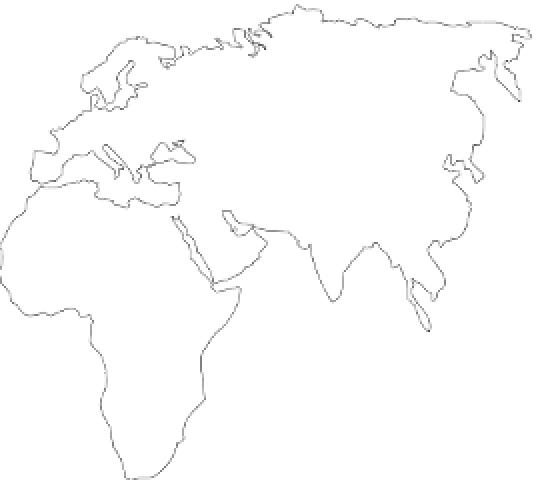
Main areas
of mangal
Main areas
of salt marsh
Figure 13.19
World distribution of salt marshes and mangals.
Source:
Adapted from Chapman (1977)