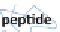Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig.
1
Schematic illustration of the glycoblotting method
1. Incubate the protein sample with 2
μ
L of protease K (0.6 U/
3.2 Release of
N -Glycans from
Glycoproteins
L) at 37 °C for 1 h, and stop the proteolysis reaction by heat-
ing at 90 °C for 10 min.
2. After cooling to room temperature, the mixture is incubated
with 5
μ
μ
l of glycopeptidase A (50
μ
U/
μ
L) at 37 °C for 16 h
(
see
Note 3
).
The “glycoblotting” method involves easily and rapidly obtaining
N
-glycan derivatives tagged with a variety of compounds from a
crude glycoprotein sample contaminated with amino acids, DNA
and RNA, etc. The hydrazide ligands (−NHNH
2
) of the BlotGlyco
beads specifi cally capture glycans digested from the glycoproteins,
and the captured glycans are labeled and released by a labeling
reagent such as aoWR (Fig.
1
).
3.3 Glycoblotting
1. Pour 500
L of BlotGlyco beads suspension onto a well of
MultiScreen Solvent fi lter plate (
see
Note 4
), and remove the
suspension solvent by vacuum.
2. Add 25
μ
μ
L of the digested mix and 1
μ
L of 50
μ
M GN4 (
see
Note 5
) to the well.
3. Add 234
L of 2 % (v/v) acetic acid/ACN to the well, and dry
up at 80 °C for 1 h (
see
Note 6
).
μ