Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
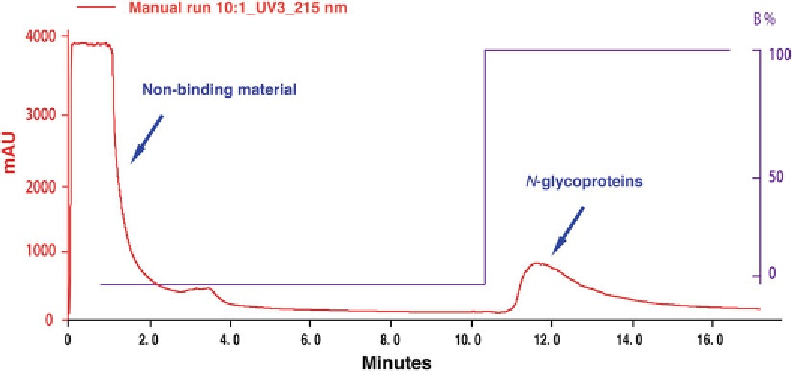
Fig.
3
A typical UV absorbance chromatogram of the
N
-glycoprotein enriched fraction from a crude protein extract
3. Centrifuge the crude extract at 15,000 ×
g
for 30 min. Recover
the supernatant and fi lter through a 0.45
m syringe fi lter. Set
aside 1 mL for a subsequent protein quantifi cation assay and
visualization by SDS-PAGE analysis.
4. Protein quantifi cation: use bicinchoninic acid (BCA,
28
) or
the Bradford assay [
29
] for protein quantifi cation, with bovine
serum albumin (BSA) to generate a standard curve.
μ
3.3 N-Glycoproteins
Enrichment Using
Lectin Cartridges
1. Equilibration step: use 10 column volumes of binding buffer
(50 mL of binding buffer in the case of 5 mL chromatography
cartridges) at a fl ow rate of 0.08 mL/min (
see
Note 2
).
2. Loading step: samples should be loaded slowly to increase
binding of the glycoproteins to the lectins (
see
Note 3
). Collect
the fl ow through for subsequent analysis by SDS-PAGE.
3. Washing step: wash the column with ten column volumes of
binding buffer, or until the absorbance at 280 nm returns to
the baseline value.
4. Elution step: elute the bound protein with fi ve column volumes
of elution buffer at a fl ow rate of approximately 0.75 mL/min.
Collect 1 mL fractions. A typical elution chromatogram of
glycoproteins is shown in Fig.
3
.
3.4 N-Glycoprotein
Batch Enrichment
1. Equilibration step: Mix 150
L of Con A slurry (commercially
obtained lectin resins are typically shipped as a suspension with
20 % ethanol as a preservative) with 5 mL of binding buffer in
a 15 mL tubes. Briefl y shake the suspension and centrifuge at
1,000 ×
g
for 2 min. Discard the supernatant and repeat the
process twice more for a total of three incubations/washes.
μ