Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig.
1
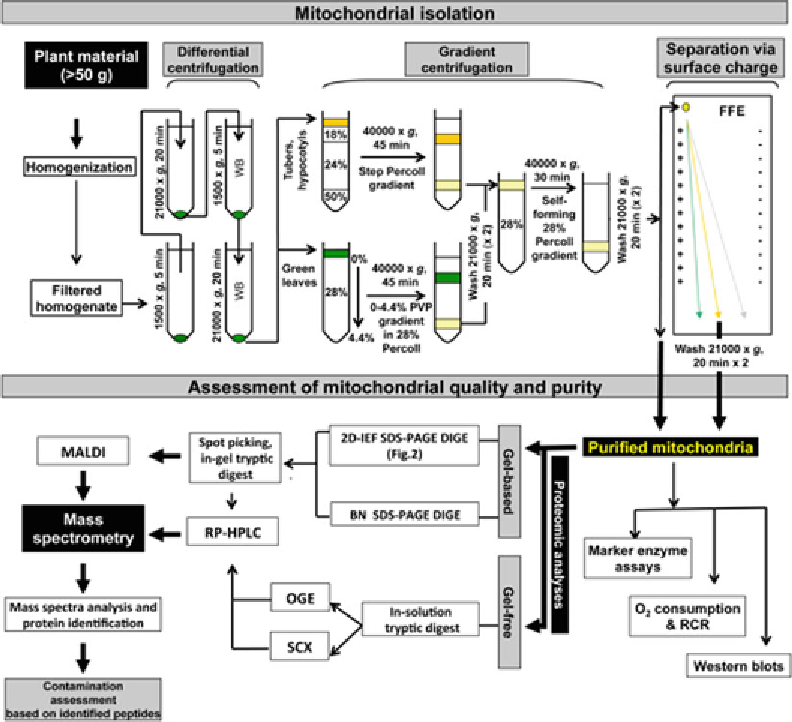
Overview of the workfl ow for the purifi cation of plant mitochondria and the determination of their quality
and purity. Plant material is homogenized in extraction buffer and the homogenate is fi ltered. The resulting
homogenate is centrifuged fi rst at low speed and then at high speed, which is repeated to generate a crude
organelle pellet. The organelles are further separated by gradient centrifugation using step or continuous gradi-
ents depending on the original plant material. The resulting mitochondria fraction is washed and collected as
purifi ed mitochondria. Further purifi cation of mitochondria can be carried out using free fl ow electrophoresis (FFE)
depending on the accessibility of hardware and the objective of experiment. The quality and purity of isolated
mitochondria can be determined by specifi c marker enzyme assays, O
2
consumption and RCR calculations and
western blots. For proteomic analysis, the purifi ed mitochondria can be separated using gel-based or gel-free
methods. For gel-based method, BN-SDS-PAGE-DIGE and 2D-IEF-SDS-PAGE-DIGE are normally used. The gel
spots containing mitochondria proteins are collected and digested with trypsin for further mass spectrometry
analysis. For gel-free method, whole mitochondria are digested with trypsin and then can be separated by off-gel
electrophoresis (OGE) or strong cation exchange (SCX) prior to RP-HPLC and mass spectrometry analysis
in-gel electrophoresis (DIGE) or spectral counting approaches. An
overview of the workfl ow for the isolation of plant mitochondria,
fractionation of proteins/peptides, and determination of contami-
nants is presented in Fig.
1
.