Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
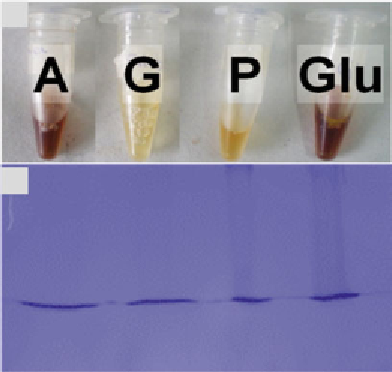
A G P GLU
Fig. 2
(
a
) Aspects of each protein fraction obtained.
A
Albumins,
G
Globulins,
P
Prolamins,
Glu
Glutelins. (
b
) Gel precleaning. 100
g of each fraction (Albumins, A;
Globulins, G; Prolamins, P; Glutelins, Glu) obtained with the protein were cleaned
in a 5 % SDS-PAGE that was further stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Labeled
proteins bands were cut from the gel and analyzed by LC coupled to MS/MS
μ
3. Centrifuge at 15,000 ×
g
for 15 min (4 °C), and transfer the
supernatant to a new tube (
see
Note 9
).
4. Repeat
steps 4
-
6
of the albumin fraction solubilization to
obtain the prolamin fraction.
1. Add 50 mL of ES4 to the pellet obtained in the
step 3
(Subheading
3.2.4
).
2. Sonicate the mixture (while keeping on ice) for 15 s (50 W,
amplitude 60), and shake in an orbital shaker for 2 h at room
temperature.
3. Centrifuge at 15,000 ×
g
for 15 min (4 °C), and transfer the
supernatant to a new tube (
see
Note 9
).
4. Repeat
steps 4
-
6
of the albumin fraction solubilization to
obtain the pellet corresponding to the glutelin fractions (
see
Note 13
).
3.2.5 Solubilization
of the Glutelin Fraction
(
see
Note 14
)
3.3 Protein
Solubilization
In all cases dried pellets resulting from each protein fraction pre-
cipitation were weighed and suspended in 7 M urea, 2 M thiourea,
4 %(w/v) CHAPS, 2 % (v/v) Triton X-100, 100 mM DTT at a
(w/v) ratio of 1:2 (
see
Note 15
). Then, they were shaken for 1 h
to facilitate protein solubilization. Once the pellet was solubilized
and the insoluble material eliminated by centrifugation (
see
Note
16
) (Fig.
2a
), the protein content was quantifi ed by the Bradford
methods [
19
], using bovine albumin as standard.