Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
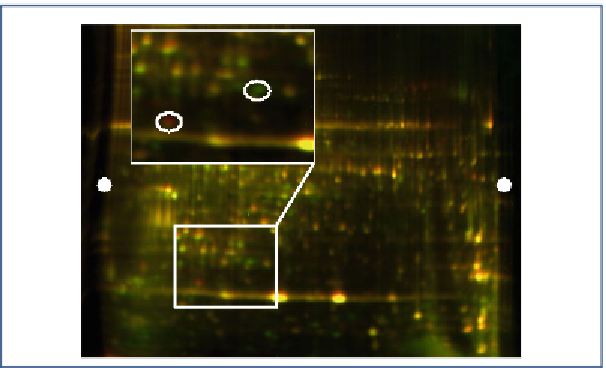
Fig.
2
Overlay of the samples containing proteins extracted from red cabbage, as seen in Fig.
1
, with a magni-
fi ed view showing proteins more abundant in the Cy3-labelled sample (in
red
) and some more abundant in the
Cy5-labelled samples (in
green
). Proteins showing comparable relative abundance are appearing in
yellow
dyeagnostics (Halle, DE), although not considered as equally
powerful as Cydyes, in our case. These labels have different molec-
ular weights and this feature may be corrected by a software device.
In conclusion, it is of primary importance to correctly plan the
experimental design, the number of samples needed, the extraction,
the homemade solutions, and the time needed for the different steps.
Approximately 300 mg of plant fresh material is crushed in liquid
nitrogen, in cold room, and treated with cold extraction buffer
(20 % TCA, 0.1 % DTT, acetone). Proteins are allowed to precipi-
tate overnight at −20 °C. After centrifugation (30,000 ×
g
; 45 min
at 4 °C), the pellet is washed with rinsing buffer (acetone/DTT
0.1 %) three times. The supernatant is discarded and the pellet is
dried in vacuo.
3.1 Extraction
of the Proteins
3.1.1 TCA/Acetone
Precipitation
300-500 mg of plant fresh material is crushed, in cold room.
200 mg of PVPP and 2 mL SDS buffer preheated at 65 °C are
added to samples. This mixture is vortexed for 5 min and subse-
quently put on ice for 15 min. After centrifugation at 15,000 ×
g
for 15 min the supernatant is kept and a re-extraction of the pellet
is performed with the same method. The obtained supernatant can
be pooled with the fi rst one. Proteins are allowed to precipitate
overnight at −20 °C by adding 8 mL of precipitation buffer I.
Samples are centrifuged (45 min, 30,000 ×
g
, 4 °C). The pellet is
washed the same two times. The supernatant is discarded and the
pellet is dried in vacuo.
3.1.2 HOT-SDS
Extraction