Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
Mr
Ctrl
pH4
pH7
pH9
kDa
132
24
108
128
236
250
150
100
75
50
37
C
pH7
25
20
15
10
pH4
183
54
10
107
37
56
4
63
13
pH9
136
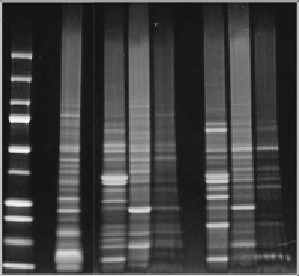
Fig.
3
Spinach proteome investigation from spinach leafs. After removal of undesired vegetable material, the
proteins were treated with CPLL at different pHs and analyzed by SDS-PAGE (
a
). Ctrl means control or untreated
protein isolate; the
arrows
indicate the positioning of RuBisCO light and heavy subunits.
Mr
: protein mass lad-
der. (
b
) Venn diagram of found proteins using LC-MS/MS as analytical method. The
circle
on the
left
represents
proteins identifi ed from untreated protein isolate, while the
circle
on the
right
represents the identifi ed proteins
upon complete CPLL treatment. (
c
) Venn diagram of identifi ed proteins upon CPLL treatment at different pH
where the contribution of each pH is shown. Many proteins are common among two or three eluates; others
are exclusive of each capture pH (adapted from [
41
] )
Native CPLL
a b c
Carboxyl. CPLL
a b c
Mr
Ctrl
250
Ctrl
235
150
100
75
48
35
16
50
37
136
15
21
25
28
20
Native CPLL
214
Carboxylated CPLL
235
15
10
Fig.
4
Hevea brasiliensis
latex proteome study. After removal of undesired material, proteins were treated with
CPLL under physiological conditions; the captured proteins were desorbed sequentially and analyzed by SDS-
PAGE (
left
). Ctrl means control or untreated protein isolate;
Mr
: protein mass ladder. The protein isolate was then
treated sequentially on two distinct CPLLs (native and carboxylated). The captured proteins were in both cases
eluted sequentially using 1 M NaCl (
a
), 2 M thiourea, 7 M urea, 3 % CHAPS (
b
), 9 M urea in 50 mM citric acid,
pH 3.3 (
c
).
Right
: Venn diagram of found proteins using LC-MS/MS as analytical method (adapted from [
23
] )