Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
2.4 Protein
Resuspension
and Solubilization
1. Solubilization buffer: 7 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 4 % (w/v)
CHAPS, 40 mM DTT, 0.5 % (v/v) carrier ampholytes
pH 3-10, and 0.002 % (w/v) bromophenol blue.
2. Refrigerated ultracentrifuge Beckman TL-100 (catalog num-
ber: 346457, Beckman Instruments, Palo Alto, CA, USA) or
similar, equipped with a rotor for 2 mL centrifuge tubes.
3
Methods
3.1 Tissue
Homogenization and
Protein Extraction
1. Homogenize plant tissues (0.1 g) to a very fi ne powder in a
liquid nitrogen-precooled mortar by using a pestle.
2. Transfer the powder to a 2 mL microcentrifuge tube and add
1.5 mL of extraction buffer. Mix well and stir in a magnetic
stirrer for 1-6 h at 4 °C.
3. Centrifuge at 20,000
g
for 30 min at 4 °C.
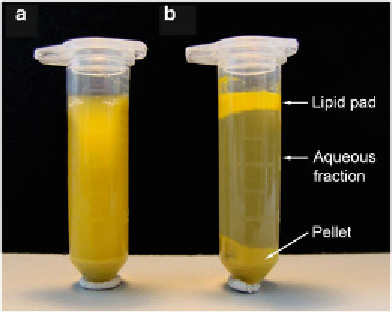
4. After centrifugation, collect the aqueous supernatant using a
syringe with a very fi ne needle and without disturbing the
upper lipid pad formed during centrifugation (Fig.
2
).
×
1. Equilibrate the column with 25 mL of equilibration buffer.
Discard the fl ow-through.
2. Add sample to the column and allow the sample to enter the
packed bed completely (
see
Note 8
). If sample volume is less
than 2.5 mL, add equilibration buffer to adjust the volume up
3.2 Protein Filtration
Fig.
2
(
a
) Protein extracts prepared from olive pollen contain large amounts of
lipids. (
b
) After centrifugation, three fractions are distinguishable: a pellet of cell
debris at the
bottom
, an aqueous supernatant in the
middle
, and a lipid pad fl oat-
ing as a
top layer
. The protein-containing aqueous fraction can be carefully col-
lected using a syringe with a very fi ne needle