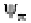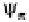Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
where
is the gravitational potential‚
is the matric potential due to adsorptive
and capillary forces‚
is the osmotic potential due to the presence of solutes‚
is
the pressure potential as in applied air or hydraulic pressure and is the overburden
pressure resulting from the weight of the overlying material and is of importance in
swelling soils. At the scale of a soil sample‚ only and are normally of importance‚
although assumes great biological importance in salt-affected soils.
The water potential of a defined mass of soil water is related to the work required
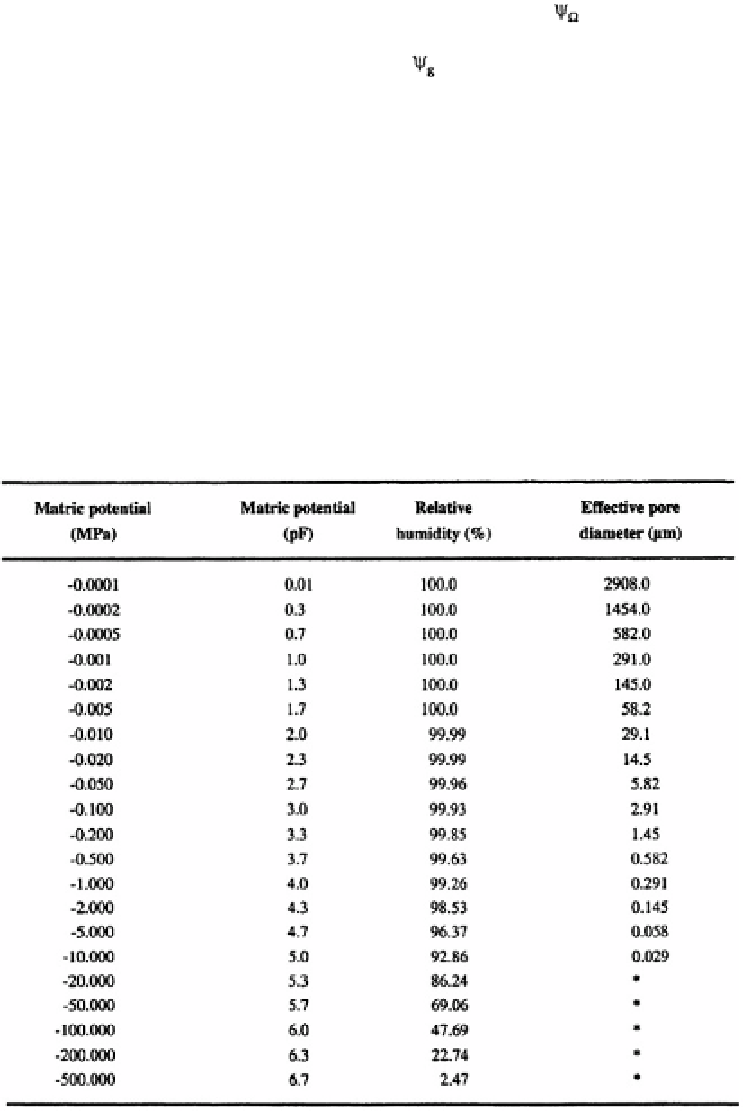
to extract it. Water potential may be expressed in any pressure unit (bars‚ centimetres of
water‚ or the S.I. unit‚ the Pascal (Pa) or in pF units which are the logarithms (to base 10)
of soil water potential expressed in centimetres of water (Table I.12). This table also
presents the sizes of the pores that remain full of water at a range of specific potentials.
Water potential in unsaturated soils is almost always negative although the numerically
equivalent positive term 'water tension' is sometimes used for convenience. Water poten-
tial is formally defined as the equivalent pressure that must be applied to the soil water
to bring it to hydraulic equilibrium through a porous membrane with a reference body
of free water (Soil Science Society of America‚ 1997). Soil water potential values
presented here will be expressed in megapascals (MPa).