Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
microbial colonisation posed by lignin-rich structures and waxy cuticles. The effects of
these materials on decomposition dynamics are detailed in Section IV.1.3.3.
Decomposition rates measured‚ for example‚ as the respiration rates of microbial
decomposers‚ or C losses from decomposing residues‚ may be described as decreasing
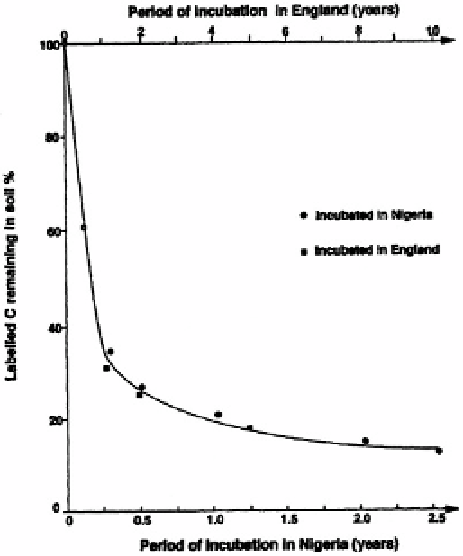
functions of time. Jenkinson and Ayanaba (1977) calculated the following double
exponential equation to describe mass loss in uniformly
labelled Rye Grass (
Lolium
perenne)
mixed with soil in England and Nigeria:
where y is % C remaining and t is time in years.
This double exponential model describes a two-compartment model‚ in which about
70 % of the plant material decomposes with a half-life of 0.25 years and the remainder
with a half-life of 8 years. Interestingly‚ the authors found that decomposition curves for
each location only differed in their time scales‚ rates being four times higher in the tropical
site (Figure IV.4). In these experiments‚ the Rye Grass samples were decomposing only
under the influence of micro-organisms; roots and macro-invertebrates were not allowed
to enter the tubes within which the grass samples were decomposing.